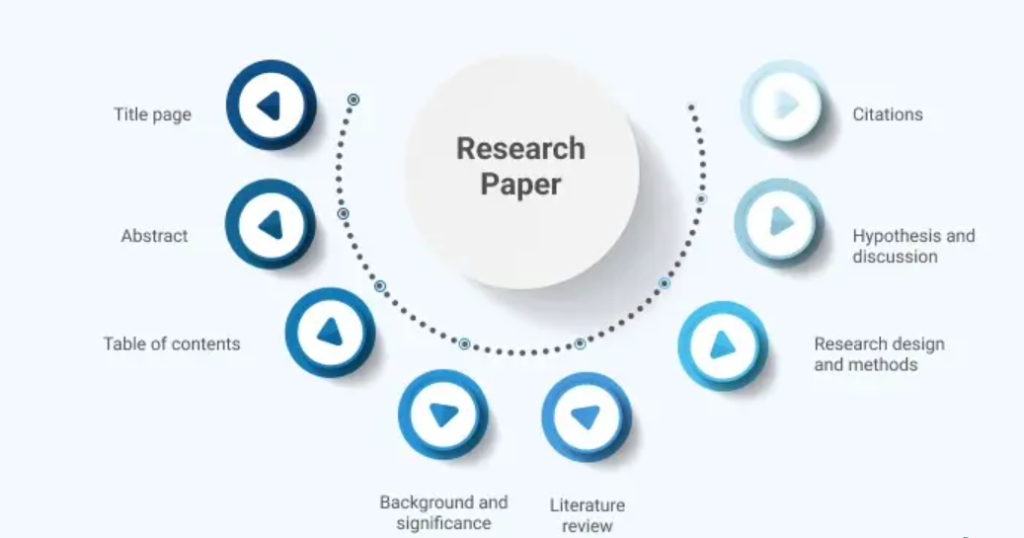
Table of Contents
Nursing is a profession deeply intertwined with leadership. Effective leadership in nursing is crucial for delivering high-quality patient care, fostering a positive work environment, and driving positive change within healthcare systems. Writing a compelling paper about leadership in nursing requires a structured approach, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the nuances of the topic.
This article provides a comprehensive guide, leading you through each stage of the process, from choosing a topic to submitting your final draft.
Steps to Crafting a Paper about Leadership in Nursing
I. Choosing Your Focus: Defining Leadership in Nursing
The broad scope of “leadership in nursing” necessitates a focused approach. Before embarking on your paper, carefully consider your area of interest. This could be a specific leadership style, a particular challenge faced by nurse leaders, the impact of leadership on patient outcomes, or the role of leadership in navigating specific healthcare contexts. Some potential areas of focus include:
- Transformational Leadership in Nursing: Explore how transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Analyze the impact of this leadership style on staff morale, patient satisfaction, and overall healthcare quality.
- The Role of Leadership in Nursing in Crisis Management: Examine how effective leadership in nursing helps navigate critical incidents, such as natural disasters, pandemics, or major medical emergencies. Focus on decision-making processes, communication strategies, and team coordination.
- Leadership in Nursing and Technology Integration: Investigate how nursing leaders facilitate the adoption and effective utilization of new technologies in healthcare settings. Analyze the challenges and opportunities presented by technological advancements and their impact on patient care and workflow efficiency.
- Ethical Leadership in Nursing: Explore the ethical considerations faced by nurse leaders and discuss strategies for promoting ethical decision-making and fostering a culture of integrity within nursing teams. This could involve exploring issues such as patient advocacy, resource allocation, and end-of-life care.
- Leadership Development Programs for Nurses: Evaluate the effectiveness of different leadership development programs designed to equip nurses with the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in leadership roles. This might involve comparing different approaches or examining the impact of specific programs on leadership skills and career advancement.

Defining your specific focus will help you refine your research and ensure your paper remains concise and impactful. Remember, the more specific your topic, the easier it will be to manage the scope of your research and writing.
II. Conducting Thorough Research: Evidence-Based Leadership in Nursing
Once you have a clearly defined focus, you need to conduct comprehensive research. This involves exploring relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and credible online resources. Focus on peer-reviewed journals for the most reliable and up-to-date information on leadership in nursing.
Use keywords relevant to your chosen focus when searching academic databases such as PubMed, CINAHL, and Scopus. Some useful keywords might include: “transformational leadership nursing,” “nurse manager leadership styles,” “evidence-based leadership nursing practice,” “leadership development nursing,” or “leadership in nursing education.” Combine these keywords to narrow your search and refine your results.
Remember to critically evaluate the sources you find. Consider the author’s credentials, the publication date, the methodology used, and the overall credibility of the information presented. Note down the key findings and arguments from your sources, ensuring proper citation to avoid plagiarism. This rigorous approach will strengthen the credibility of your paper and demonstrate your understanding of leadership in nursing.
III. Structuring Your Paper: A Logical Flow for Leadership in Nursing Research
A well-structured paper is crucial for effectively communicating your research findings. A typical structure includes:
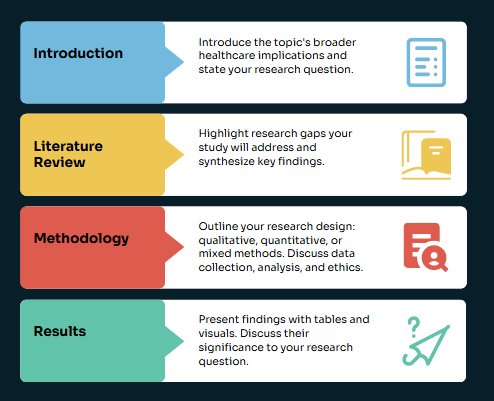
- Introduction: This section should introduce the topic of your paper, provide background information on leadership in nursing, state your research question or thesis statement, and outline the structure of your paper. Clearly define your understanding of leadership in nursing within this context.
- Literature Review: This is a critical section where you synthesize existing research relevant to your topic. Present a clear overview of the current literature, highlighting key themes, debates, and gaps in knowledge. This section should support your thesis and provide a foundation for your own analysis.
- Methodology (if applicable): If your paper involves primary research (e.g., surveys, interviews, case studies), you need a dedicated methodology section. Describe your research methods, your sample population, your data collection techniques, and your data analysis methods.
- Results (if applicable): If your paper presents primary research findings, this section should present your results clearly and concisely, using tables, charts, or graphs where appropriate.
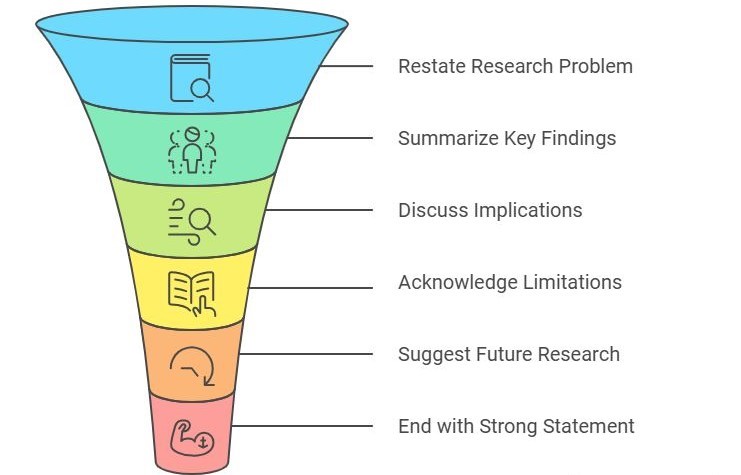
- Discussion: This is where you interpret your findings in relation to the existing literature. Discuss the implications of your research, consider any limitations of your study, and suggest areas for future research. This section should tie back to your initial research question or thesis statement.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main findings and restate your conclusions in a concise and impactful way. Highlight the significance of your research and its implications for leadership in nursing practice.
- References: List all the sources you cited in your paper using a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
IV. Writing Style and Tone: Communicating Effectively about Leadership in Nursing
Clarity and precision are key to effective writing. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly technical terms unless necessary and clearly defined. Maintain a formal and objective tone throughout your paper, supporting your arguments with evidence from your research. Ensure your writing flows logically and smoothly, guiding the reader through your arguments and analysis.
V. Revising and Editing: Polishing Your Paper on Leadership in Nursing
Once you have completed your first draft, it’s crucial to revise and edit your paper carefully. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inconsistencies in style. Ensure that your arguments are well-supported by evidence and that your writing is clear, concise, and engaging. Consider seeking feedback from peers or professors to identify areas for improvement. Proofreading is crucial for ensuring a polished and professional final product. Careful attention to detail will reflect well on your understanding of the topic of leadership in nursing.
Addressing the Challenges of Leadership in Nursing
Writing about leadership in nursing requires acknowledging the inherent complexities and challenges of the role. Your paper could explore these challenges directly, providing valuable insights into the difficulties faced by nurse leaders. For example, you could discuss:
- Balancing patient care with administrative responsibilities: Nurse leaders often grapple with managing their clinical duties alongside their managerial responsibilities.
- Managing diverse teams: Leading diverse teams with varied backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives requires strong interpersonal skills and cultural sensitivity.
- Navigating organizational politics: Nurse leaders must navigate complex organizational dynamics and advocate for their teams and patients within the limitations of their resources.
- Maintaining work-life balance: The demanding nature of leadership in nursing often leads to challenges in maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
- Addressing staff shortages and burnout: Many nurse leaders face the considerable challenge of managing staff shortages and combating the widespread issue of burnout among their teams.
Addressing these challenges will make your paper more nuanced and relevant to the lived experiences of nurse leaders. It provides a more complete picture of leadership in nursing and its practical applications.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Writing About Leadership in Nursing
Nursing leadership is a complex and multifaceted field, demanding both strong clinical skills and effective management capabilities. Writing a compelling and insightful paper on this topic requires careful planning and execution. Many aspiring authors stumble over common mistakes that can significantly detract from the quality and impact of their work. Avoiding these pitfalls is crucial to producing a paper that truly reflects the nuances of leadership in nursing and contributes meaningfully to the existing literature.
1. Lack of a Clear Focus and Thesis Statement
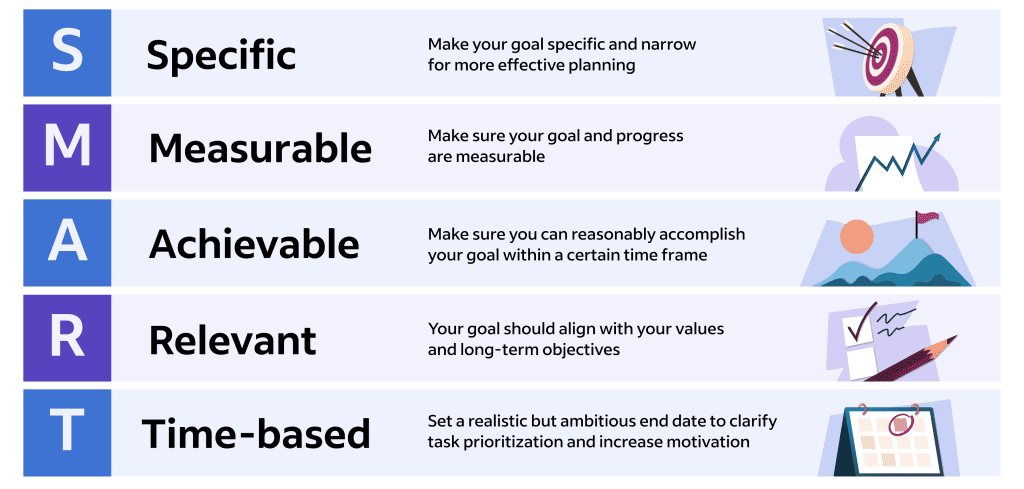
One of the most frequent errors is failing to establish a concise and focused thesis statement. Leadership in nursing encompasses a vast array of topics, from ethical considerations to organizational management and team dynamics. Without a clearly defined research question or argument, your paper risks becoming a rambling collection of loosely related ideas. Before you begin writing, meticulously identify the specific aspect of leadership in nursing you wish to explore. This focus will guide your research and ensure coherence throughout your paper. A strong thesis statement will clearly articulate your central argument and provide a roadmap for the reader.

2. Over-Reliance on Generalizations and Anecdotal Evidence
While personal experiences can provide valuable context, relying solely on anecdotal evidence weakens the academic rigor of your paper. Strong arguments require robust empirical support. Your paper must draw upon credible research, scholarly articles, and established theories of leadership and management. Avoid making broad generalizations about leadership in nursing without backing them up with substantial evidence. For example, instead of stating that “nurses are naturally good leaders,” delve into specific research that explores the correlation between nursing education, personality traits, and effective leadership styles.
3. Neglecting Theoretical Frameworks
Integrating relevant leadership theories into your analysis is crucial for providing a solid foundation for your arguments. Familiarize yourself with established models, such as transformational leadership, servant leadership, or situational leadership, and consider how these frameworks can be applied to the context of nursing leadership. Applying a theoretical lens enables you to analyze your chosen topic with depth and sophistication, moving beyond simple descriptions to insightful interpretations. Ignoring theoretical frameworks often results in superficial analysis and limits the overall impact of your paper.
4. Inadequate Literature Review
A thorough literature review is the cornerstone of any academic paper. A comprehensive review demonstrates your understanding of existing research and situates your work within the broader scholarly conversation. Simply listing a series of articles is insufficient. You need to critically evaluate the existing literature, identifying key themes, debates, and gaps in the research. This critical analysis will help you to refine your research question and justify the contribution of your own work to the field of leadership in nursing. A well-structured literature review adds significant weight and credibility to your paper.

5. Poor Organization and Structure
A well-structured paper is essential for clarity and readability. Follow a logical progression of ideas, ensuring smooth transitions between sections. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide the reader and enhance comprehension. Your arguments should be presented in a coherent and persuasive manner, building upon previous points to reach a compelling conclusion. Poor organization can confuse the reader and undermine the impact of your research on leadership in nursing.
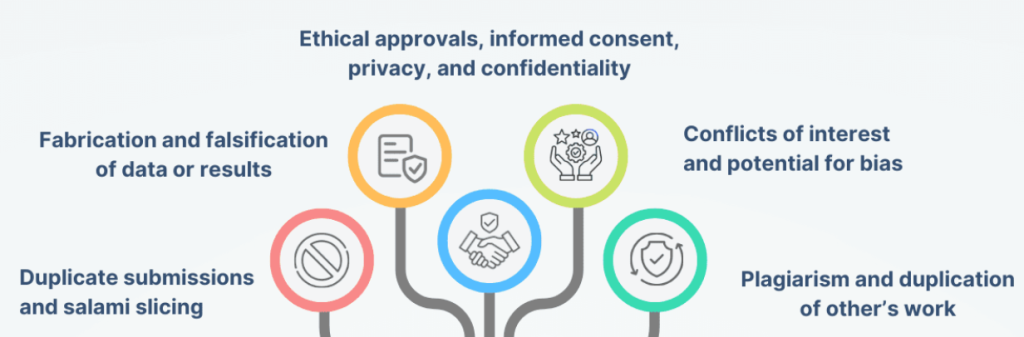
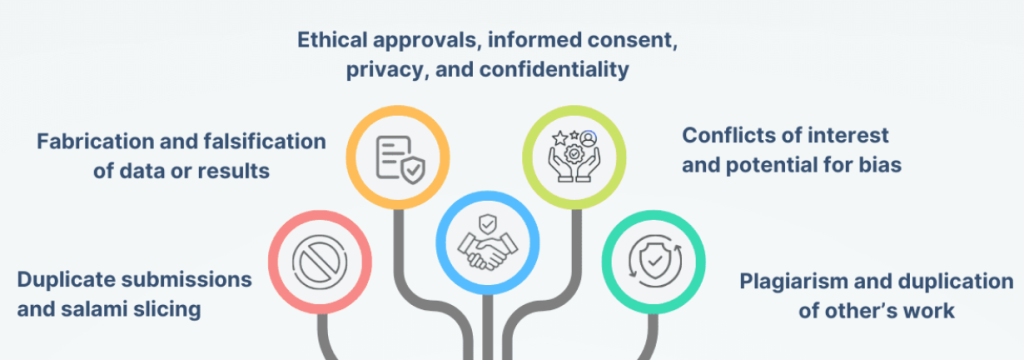
6. Ignoring Counterarguments and Limitations
A truly strong paper acknowledges and addresses potential counterarguments to your thesis. Demonstrating an awareness of opposing viewpoints strengthens your credibility and showcases a nuanced understanding of the subject matter. Furthermore, acknowledging the limitations of your research, such as sample size or methodological constraints, enhances the integrity of your work. Ignoring these aspects can weaken your paper’s overall persuasiveness and leave it vulnerable to criticism.
Avoiding these common pitfalls can significantly enhance the quality and impact of your paper on leadership in nursing. Remember that meticulous research, clear articulation of your arguments, and a robust theoretical framework are key ingredients in producing a paper that contributes meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge in this vital field.
The Enduring Importance of Leadership in Nursing
Writing a paper on leadership in nursing is an opportunity to contribute to the body of knowledge surrounding this vital aspect of the healthcare profession. By focusing on a specific area of interest, conducting thorough research, and structuring your paper logically, you can produce a compelling and insightful piece of work. Remember, leadership in nursing is not simply about managing tasks; it is about inspiring and empowering individuals to achieve shared goals, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a more fulfilling work environment.
Effective leadership in nursing is essential for the advancement of the profession and the well-being of those it serves. The challenges are significant, but the rewards of fostering effective leadership in nursing are immeasurable. Through careful research and thoughtful analysis, your paper can contribute to the ongoing conversation about best practices and future advancements in this critical field. Leadership in nursing is a crucial topic that warrants continued attention and exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions about Leadership in Nursing
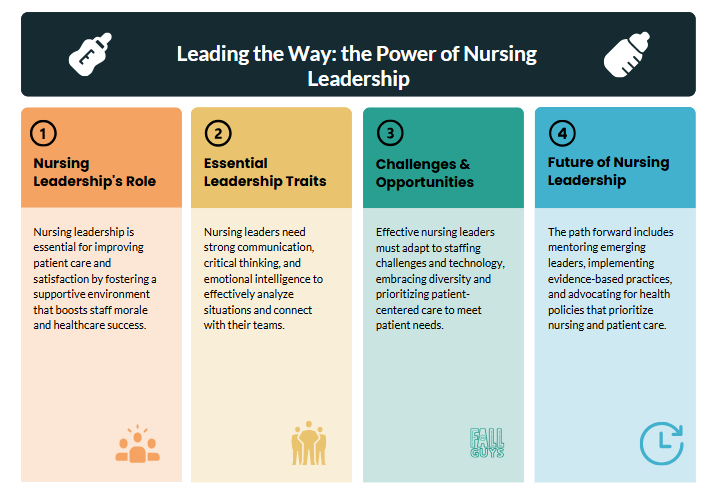
Leadership in nursing is a multifaceted role, demanding a unique blend of clinical expertise, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking. Aspiring and current nurses often grapple with similar questions regarding their leadership journey. This article addresses some frequently asked questions to provide clarity and guidance.
Q1: What exactly is meant by “leadership in nursing”?
Leadership in nursing encompasses a broad spectrum of responsibilities beyond direct patient care. It involves influencing, motivating, and guiding individuals and teams to achieve shared goals within a healthcare setting. This can manifest in various ways, from leading a small team on a unit to managing an entire department, or even advocating for policy changes at an organizational or national level. Effective leadership in nursing focuses on creating a positive work environment, fostering collaboration, ensuring patient safety, and promoting professional development.
Q2: Is leadership in nursing only for those in management positions?
Absolutely not. While formal management roles offer significant leadership opportunities, leadership in nursing can and should be demonstrated at all levels. Staff nurses can exhibit leadership through mentorship, precepting new colleagues, proactively identifying and addressing safety concerns, and advocating for their patients. Every nurse has the potential to influence and inspire others, contributing to a positive and efficient healthcare team. This distributed form of leadership is increasingly valuable in modern healthcare.
Q3: What are the key skills required for successful leadership in nursing?
Successful leadership in nursing requires a diverse skill set. Clinical expertise is foundational, allowing for informed decision-making and credible influence. However, effective communication, both verbal and written, is paramount for clear direction and collaborative problem-solving. Strong interpersonal skills are crucial for building trust, fostering teamwork, and managing conflict constructively. Critical thinking and problem-solving abilities are essential for navigating complex situations and making timely, informed decisions. Finally, adaptability and resilience are crucial for handling the unpredictable nature of healthcare. Leadership in nursing also requires emotional intelligence – the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and empathize with others.
Q4: How can I develop my leadership skills in nursing?
There are numerous avenues for developing leadership in nursing. Formal education, such as pursuing a Master’s degree in nursing administration or a leadership certificate, provides structured learning and theoretical foundations. However, practical experience is equally important. Seeking out mentorship opportunities, actively participating in committees, and volunteering for leadership roles within professional organizations provide invaluable real-world experience. Reflecting on your experiences, identifying areas for improvement, and seeking feedback from colleagues are critical for continuous growth. Attending workshops and conferences focused on leadership skills can also significantly enhance your capabilities.
Q5: What are the challenges faced by nurses in leadership positions?
Nurses in leadership positions face numerous challenges. Balancing the demands of administrative tasks with the need for direct patient care can be demanding. Managing staff, navigating complex organizational politics, and dealing with limited resources require strong leadership and strategic thinking. Burnout and compassion fatigue are prevalent risks, necessitating robust self-care strategies and organizational support. Advocating for staff needs while also meeting organizational goals presents a constant balancing act. Effective leadership in nursing involves navigating these complex issues with skill and grace.
Get Help with Writing a Nursing Leadership Paper
Are you struggling with writing a nursing leadership paper? Then, engage our experts at Nursing Papers for professional help. We offer customized help with nursing research papers, essays, case studies and dissertations. Our service covers topic suggestion, paper writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Get in touch with us today to order a customized nursing leadership paper.