Table of Contents
A critical review nursing paper is a crucial academic exercise that delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and implications of a specific nursing research study, policy, or intervention. It goes beyond summarizing the chosen work and provides a rigorous analysis that demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter and your ability to critically evaluate research.
This article will guide you through the essential steps and considerations for crafting a compelling and informative critical review nursing paper. These guidelines will enable you to confidently approach this academic endeavor and produce a paper that reflects your critical thinking and analysis skills.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Critical Review Nursing Paper
Step 1: Selecting Your Topic and Research Question
The first step in writing a critical review nursing paper is to select a relevant topic and formulate a focused research question. Choosing a subject that aligns with your interests and research goals will enhance your engagement and ensure the quality of your paper.
Tips for Topic Selection:
- Relevance: Choose a topic that is relevant to current nursing practice, education, or research.
- Specificity: Narrow your topic down to a specific area of focus, such as a particular nursing intervention, patient population, or healthcare setting.
- Availability of Resources: Ensure that sufficient research articles, policies, or interventions are available for your critical review.
Formulating a Research Question:
- Clear and Concise: Your research question should be clearly stated and easily understood.
- Focused: It should be specific enough to guide your analysis and prevent your paper from becoming too broad.
- Answerable: The question should be answerable using available resources.
Example Research Question:
- “What are the strengths and limitations of using aromatherapy as a complementary therapy for managing anxiety in patients undergoing surgery?”
Step 2: Gathering and Analyzing Your Resources
Once you have a topic and research question, you need to gather and analyze relevant resources for your critical review nursing paper. This involves identifying, evaluating, and critically assessing the available literature, policies, or interventions.
Identifying Resources:
- Databases: Use relevant databases such as CINAHL, PubMed, and Cochrane Library to find research articles, systematic reviews, and clinical practice guidelines.
- Professional Journals: Explore nursing journals to locate articles that focus on your chosen topic.
- Government Agencies: Access websites of organizations like the National Institute of Health (NIH) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for relevant research and guidelines.
- Grey Literature: Include reports from government agencies, think tanks, and non-profit organizations that may provide valuable insights.
Evaluating Resources:
- Credibility: Assess the source’s reputation, author qualifications, and publishing venue to determine its trustworthiness.
- Relevance: Ensure the resource directly addresses your research question and provides relevant information.
- Methodology: Evaluate the research methods used in the study to ensure their quality and rigor.
- Bias: Be aware of potential biases that may influence the findings or conclusions of the study.
Analyzing Resources:
- Critical Reading: Analyze the content of each resource, identifying key findings, strengths, weaknesses, and implications.
- Synthesis: Synthesize the information from multiple sources to develop a comprehensive understanding of your topic.
- Comparison and Contrast: Compare and contrast different perspectives, findings, and methodologies to highlight similarities and differences.
Step 3: Structuring Your Critical Review Nursing Paper
The structure of your critical review nursing paper is crucial for effectively presenting your analysis and findings. A logical and clear structure helps readers follow your arguments and comprehend your critical evaluation.
Typical Structure:
- Introduction:
- Background: Provide a brief overview of the topic and its significance in nursing practice.
- Purpose: State the purpose of your paper, which is to critically review the chosen research study, policy, or intervention.
- Research Question: Clearly state your research question.
- Literature Review:
- Key Concepts: Define and explain key concepts related to your topic.
- Summary of Existing Research: Summarize and synthesize the findings of relevant studies, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each.
- Critical Analysis:
- Methodological Strengths: Discuss the strengths of the study’s methodology, such as appropriate sample size, robust data collection techniques, and rigorous data analysis.
- Methodological Weaknesses: Identify and analyze potential weaknesses in the study’s methodology, such as sampling bias, limited data, or inappropriate statistical analysis.
- Findings: Discuss the main findings of the study, considering their significance and limitations.
- Implications for Practice: Analyze the implications of the study’s findings for nursing practice, education, or research.
- Ethical Considerations: Address any ethical considerations related to the study or intervention.
- Conclusion:
- Summary: Briefly summarize the main points of your critical review nursing paper.
- Recommendations: Provide recommendations for further research, practice, or policy development based on your analysis.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations of your review, such as potential biases or a limited scope of resources.

Step 4: Writing Your Critical Review Nursing Paper
Once you have structured your paper, you need to write clear and concisely. This involves conveying your critical analysis in a professional and scholarly tone.
Writing Tips:
- Clarity: Use clear and precise language, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Objectivity: Maintain an objective tone, avoiding personal opinions or biases in your analysis.
- Evidence-Based: Support all claims with credible evidence from your resources, using appropriate citations.
- Logical Flow: Organize your ideas in a logical sequence, transitioning smoothly between paragraphs and sections.
- Academic Style: Follow the guidelines for academic writing, including proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
Step 5: Editing and Proofreading
After writing your critical review nursing paper, it’s crucial to edit and proofread your work to ensure clarity, accuracy, and professionalism.
Editing Tips:
- Content: Ensure that the content is comprehensive, well-organized, and relevant to your research question.
- Clarity: Check for clarity and conciseness in your writing, eliminating any ambiguity or redundancy.
- Grammar and Spelling: Carefully proofread for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and punctuation issues.
- Citation Style: Ensure that all sources are cited correctly according to the chosen citation style, such as APA or MLA.
Step 6: Submitting Your Critical Review Nursing Paper
Finally, submit your critical review nursing paper according to the instructions provided by your instructor or institution.
Submission Tips:
- Formatting: Follow the formatting guidelines for font, margins, spacing, and headings.
- Deadline: Submit your paper by the specified deadline, avoiding late submissions.
- Plagiarism: Ensure that your paper is original and free from plagiarism, citing all sources correctly.
Crafting a critical review nursing paper is a demanding yet rewarding academic exercise. By following these comprehensive guidelines, you can develop the skills needed to critically analyze research, policies, or interventions, effectively communicate your insights, and contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge and practice. Remember, a well-written critical review nursing paper demonstrates your analytical thinking, research skills, and understanding of the nursing profession.
Navigating the Common Pitfalls in Critical Review Nursing Papers
The critical review nursing paper is a cornerstone of academic nursing education. It’s not just about summarizing existing research; it’s about critically evaluating it, dissecting its strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately contributing to the advancement of nursing knowledge. However, this complex task can be fraught with pitfalls that can derail even the most diligent student.
Understanding these pitfalls and learning how to avoid them is crucial for crafting a high-quality critical review nursing paper. This article will explore common pitfalls and offer practical solutions for writing a paper that shines.
1. Lack of Focus: Aiming for the Bullseye
One of the most prevalent pitfalls is a lack of focus. Choosing a broad topic for your critical review nursing paper can lead to a superficial analysis. Instead, hone in on a specific research question or a targeted area within the chosen topic. This allows for a deeper dive into the literature and a more focused critical review.
Example: Instead of “The Impact of Technology on Nursing Practice,” focus on “The Influence of Telehealth on Patient Satisfaction in Chronic Disease Management.”
Solution:
- Define a clear research question or scope. This will provide a framework for your analysis and help you stay on track.
- Refine your search terms. Use specific keywords to narrow your search and identify relevant research articles.
- Consider narrowing your focus to a specific population, intervention, or outcome. This can further refine your research question and ensure a deeper analysis.
2. Inadequately Evaluating the Chosen Literature: More Than Just Summarizing
Many students fall into the trap of merely summarizing the chosen research articles. This fails to demonstrate critical thinking and analysis, which are the heart of a critical review nursing paper.
Example: Simply stating “This study found that…” or “The authors concluded that…” without critically evaluating the findings, their implications, and their limitations.
Solution:
- Go beyond summarizing the research. Engage in deeper analysis by asking:
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research methodology?
- How do the findings relate to existing knowledge in the field?
- Are there any methodological limitations that affect the reliability of the findings?
- What are the clinical implications of the findings?
- Use critical thinking skills. This includes:
- Analysis: Breaking down the research into its components.
- Synthesis: Combining different studies to form a cohesive argument.
- Evaluation: Assessing the quality and relevance of the research.
3. Neglecting the Literature Review: Building a Foundation
A thorough literature review is the cornerstone of a strong critical review nursing paper. Failing to conduct a comprehensive review can lead to a weak argument and lack of credibility.
Example: Relying on a few articles without exploring the broader body of research on the topic.
Solution:
- Start with a comprehensive search. Use multiple databases and search engines to identify relevant research articles.
- Employ a systematic approach. Utilize a framework for organizing and evaluating the literature, such as a table or matrix.
- Include a variety of sources. Consider using books, journals, conference proceedings, and grey literature.
- Consider the quality of the sources. Evaluate the credibility of the authors and publications to ensure the reliability of your information.
4. Lack of Structure and Organization: A Clear Path for the Reader
A poorly structured and disorganized critical review nursing paper can leave the reader confused and disoriented. A clear and logical structure is essential for effective communication.
Example: Jumping between different topics without a clear flow or transition.
Solution:
- Develop a clear outline. This will guide the writing process and ensure a cohesive structure.
- Use headings and subheadings. These provide a clear roadmap for the reader and help to organize the information.
- Employ transitional phrases. These smooth the flow between paragraphs and sections, enhancing the readability of the paper.
- Maintain a consistent writing style. This ensures clarity and professionalism.
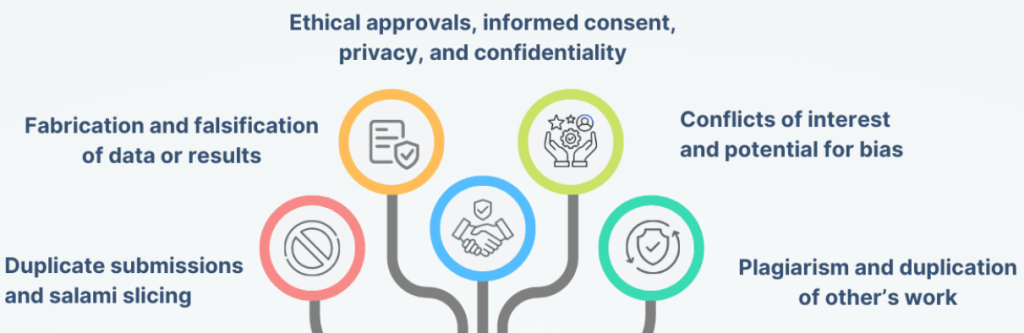
5. Ignoring Ethical Considerations: Responsible Research and Writing
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in conducting and writing a critical review nursing paper. It’s vital to acknowledge and respect the intellectual property of others and to adhere to ethical guidelines.
Example: Plagiarism, failure to properly cite sources, or misuse of research data.
Solution:
- Understand and adhere to ethical guidelines. This includes proper citation, referencing, and avoiding plagiarism.
- Utilize academic writing resources. These can help you understand and implement appropriate ethical practices.
- Use plagiarism detection software. These tools can help you identify and correct any instances of plagiarism.
6. Insufficient Evidence: Supporting Your Claims
A critical review nursing paper needs solid evidence to support its claims. Simply stating opinions without providing supporting data weakens the argument and undermines credibility.
Example: Asserting a claim without providing any research evidence to back it up.
Solution:
- Use specific examples and data points. These strengthen your argument and demonstrate the validity of your claims.
- Draw upon reputable sources. Cite evidence from peer-reviewed journals, respected organizations, and credible experts.
- Integrate evidence seamlessly. Don’t just list citations; weave them into your discussion to support your arguments.
7. Poor Writing Style: Communicating Effectively
A critical review nursing paper should be written in a clear, concise, and professional manner. Poor writing style can hinder readability and comprehension.
Example: Using jargon, overly complex sentences, or passive voice, which makes the writing sound stilted and academic.
Solution:
- Write in a clear and concise style. Use simple language and avoid unnecessary jargon.
- Employ active voice whenever possible. This makes the writing more direct and engaging.
- Proofread carefully. This helps to catch errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Consider getting feedback. Ask a colleague or instructor to review your paper for clarity and style.
8. Avoiding a Conclusion: Bringing it All Together
A strong conclusion summarizes the key findings of your critical review nursing paper and reiterates the significance of your analysis. Ignoring this critical element leaves the reader with unanswered questions.
Example: Simply restating the introduction or failing to synthesize the key insights of the review.
Solution:
- Restate your main argument and key findings. Provide a concise summary of the most important points of your analysis.
- Highlight the implications of your findings. Discuss the practical applications of the research and its relevance to nursing practice.
- Suggest future research directions. Identify areas where further research is needed and propose potential research questions.
9. Lack of Critical Engagement: Going Beyond the Surface
A critical review nursing paper requires more than just describing research findings; it demands critical engagement. Failing to go beyond surface-level analysis weakens the paper’s impact.
Example: Simply summarizing research findings without analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, or implications.
Solution:
- Apply critical thinking skills. Analyze the research methodology, evaluate the findings, and consider the limitations of the studies.
- Pose thoughtful questions. Challenge the research assumptions and explore alternative interpretations.
- Consider the broader context. Place the research in a broader historical, social, or cultural context.
10. Failing to Proofread Thoroughly: Catching the Small Errors
Proofreading is a crucial step in the writing process. Neglecting this essential step can lead to errors that detract from the overall quality of the paper.
Example: Typographical errors, grammatical mistakes, or inconsistencies in formatting.
Solution:
- Proofread carefully and meticulously. Read your paper aloud to catch any errors you might miss when reading silently.
- Consider using a spell checker and grammar checker. These tools can help identify common mistakes.
- Get feedback from a peer reviewer. This can help you identify areas where you might have missed errors.
Frequently Asked Questions about Critical Review Nursing Papers
1. What is a critical review paper in nursing?
A critical review paper in nursing is an academic essay that analyzes and evaluates existing research on a specific nursing topic. It goes beyond simply summarizing the literature, critically assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the research, highlighting gaps in knowledge, and drawing conclusions.
2. What are the key components of a critical review paper?
A well-structured critical review paper typically includes:
- Introduction: Clearly states the topic, research question, and purpose of the review.
- Literature Search Strategy: Explains the methods used to identify relevant studies, including databases, keywords, and inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Summary of Findings: Summarizes the key findings from the included studies, highlighting similarities and differences in results.
- Critical Analysis: Analyzes the strengths and limitations of the included studies, focusing on methodology, biases, and generalizability.
- Synthesis and Discussion: Synthesizes the findings and provides a critical interpretation of the overall body of literature.
- Conclusions: Summarizes the key findings and implications for nursing practice, research, and policy.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identifies areas for further investigation based on the gaps in knowledge revealed by the review.
3. What are some tips for writing a critical review paper?
- Choose a focused topic: Narrow down your research question to ensure a manageable scope for your review.
- Develop a clear search strategy: Use a systematic approach to identify relevant research, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the literature.
- Read critically: Go beyond simply summarizing the studies. Analyze the methodology, data, and conclusions critically to identify strengths and limitations.
- Organize your review logically: Structure your paper with clear headings and subheadings to guide the reader through your analysis.
- Synthesize the findings: Draw connections between the studies, highlighting the overall picture emerging from the literature.
- Present your findings concisely and effectively: Use clear language and avoid jargon.
4. How can I ensure my critical review is objective and unbiased?
- Use a balanced approach: Include both positive and negative aspects of the studies you review.
- Avoid personal opinions: Back up your arguments with evidence from the literature.
- Consider opposing viewpoints: Acknowledge alternative perspectives and address potential criticisms of your analysis.
- Be transparent about your own biases: Acknowledge any potential biases you may have that could influence your interpretation of the literature.
5. How can I find suitable sources for my critical review?
- Start with databases: Use databases like CINAHL, PubMed, and Medline to access peer-reviewed nursing research articles.
- Look for systematic reviews: These reviews provide a comprehensive overview of a specific topic, making it easier to identify key studies.
- Consult with your professor or librarian: Seek guidance and support from experts in your field.
6. What are the common pitfalls to avoid in writing a critical review?
- Lack of focus: Avoid trying to cover too much ground in one paper.
- Superficial analysis: Go beyond simply summarizing the studies; delve deeper into the strengths and limitations of the research.
- Unclear organization: Structure your review logically to guide the reader through your analysis.
- Poorly-supported arguments: Back up your claims with evidence from the literature.
- Uncritical acceptance of findings: Acknowledge the limitations of the research and potential biases.
7. How can I improve the quality of my critical review nursing paper?
- Get feedback from others: Ask a peer, professor, or writing center for feedback on your draft.
- Revise and edit carefully: Proofread for grammar, punctuation, and style errors.
- Cite your sources accurately: Use a consistent citation style and ensure all sources are properly credited.
8. What are the most important things to consider when writing a critical review?
- Relevance: Choose a topic relevant to nursing practice, research, or policy.
- Clarity: Present your ideas clearly and concisely, using language appropriate for your audience.
- Objectivity: Maintain an unbiased approach, considering all sides of the issue.
- Critical thinking: Go beyond simply summarizing the literature; analyze the strengths and limitations of the research.
- Synthesis: Draw connections between the studies and provide a cohesive interpretation of the body of literature.
- Contribution: Contribute to the understanding of the chosen topic and offer recommendations for future research.
By following these guidelines, you can write a strong and informative critical review paper that contributes to the nursing literature and demonstrates your critical thinking skills.
The Bottom Line

A critical review nursing paper is a valuable opportunity to deepen your understanding of the field and contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge. By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can craft a paper that showcases your critical thinking skills, provides a compelling analysis of the literature, and leaves a lasting impact on your readers.
Remember, the process of writing a critical review nursing paper is a journey, not a destination. Embrace the challenges, seek feedback, and refine your approach with each paper. By constantly striving to improve your writing skills, you’ll not only produce high-quality critical review nursing papers but also become a more knowledgeable and effective nurse.
Get Professional Critical Review Nursing Paper Writing Help
At Nursing Papers, we can help you to craft an authentic and impactful critical review nursing paper. Our service covers topic suggestion, paper writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Besides, we can also assist with writing nursing essays, research papers and dissertations.