Table of Contents
The nursing literature review is more than just a summary of research findings. It is a cornerstone of evidence-based practice that will form the bulk of your essay. The literature review is a critical exploration of the current state of knowledge on a specific topic, meticulously analyzing, synthesizing, and interpreting diverse perspectives to provide a comprehensive understanding of the issue. Although the process is demanding, it is essential for nurses to stay abreast of current research, inform clinical decision-making, and contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge.
What is the Purpose of a Nursing Literature Review?
The nursing literature review serves four main purposes including;
- Identifying the current body of knowledge: This involves a thorough search and evaluation of relevant literature to uncover what is already known about the topic.
- Analyzing and synthesizing the findings: Critical analysis of the literature, considering strengths and limitations, helps to identify trends, gaps, and inconsistencies in the research.
- Developing a clear understanding of the topic: Synthesizing the findings from various studies allows for a cohesive picture of the topic, highlighting areas of agreement and disagreement.
- Identifying areas for future research: By critically examining the literature, researchers can identify gaps in knowledge and propose future research questions to further advance the field.
The Foundation: Choosing a Topic and Focus:
The first step in writing a nursing literature review is selecting a topic. This choice should align with your interests, clinical practice, or current research priorities. Consider these factors when choosing a topic:
- Relevance: Is the topic relevant to current nursing practice, relevant to your area of expertise, and addressing a significant health issue?
- Feasibility: Is the topic manageable in terms of the volume of available literature, the complexity of the research, and the time frame for completion?
- Potential for Impact: Does the topic hold the potential to contribute meaningfully to nursing knowledge and practice?
Once a topic is chosen, define a clear focus for your review. This can be a specific area of interest within a broader topic, a particular patient population, or a specific intervention or outcome.
The Structure of a Literature Review
A well-structured nursing literature review presents a logical and organized approach to the topic. A common structure includes:
- Introduction: Introduce the topic and state the purpose of the review. Clearly define the scope of the review, the specific research questions being addressed, and the search criteria used to identify relevant literature.
- Literature Search and Selection: Describe the databases, search terms, and inclusion/exclusion criteria used to conduct the literature search. Explain the process of selecting relevant studies and the rationale behind any exclusions.
- Body of the Review: This section presents the findings of the literature search, organized thematically or chronologically. Each section should critically analyze and synthesize the findings of the relevant studies, highlighting key findings, methodologies, and limitations.
- Discussion and Analysis: Discuss the overall findings of the review, highlighting trends, gaps, inconsistencies, and areas of agreement and disagreement. Analyze the limitations of the research and suggest potential areas for future research.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key findings of the review and reiterate the implications for nursing practice, policy, or research. Conclude with a forward-looking statement about the importance of further research in the field.
The Content: Weaving the Threads of Knowledge
The content of your literature review should be comprehensive, analytical, and insightful. Consider these key elements:
- Critical Evaluation: Analyze the strengths and limitations of each study, including methodology, sample size, data analysis, and potential biases.
- Synthesis of Findings: Don’t simply list summaries of individual studies. Synthesize the findings to identify patterns, trends, and areas of agreement and disagreement.
- Theoretical Framework: Relate the findings to relevant nursing theories and models to provide a deeper understanding of the topic and its implications for practice.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Highlight the practical implications of the research findings for nursing practice, including potential interventions, guidelines, or recommendations.
- Ethical Considerations: Consider the ethical implications of the research findings and the impact of the research on patients, families, and society.
The Language: Crafting a Compelling Narrative
The language of a nursing literature review should be clear, concise, and objective. Avoid jargon and colloquialisms, and use descriptive language to convey the findings of the research.
- Formal and Objective Tone: Maintain a formal and objective tone throughout the review, avoiding personal opinions or biases.
- Evidence-Based Statements: Support all claims with evidence from the literature, using citations to ensure accuracy and credibility.
- Third-Person Perspective: Write in the third person, focusing on the findings of the research rather than personal opinions or interpretations.
- Use of Transitions: Use transitional phrases to connect ideas, enhance flow, and guide the reader through the review.
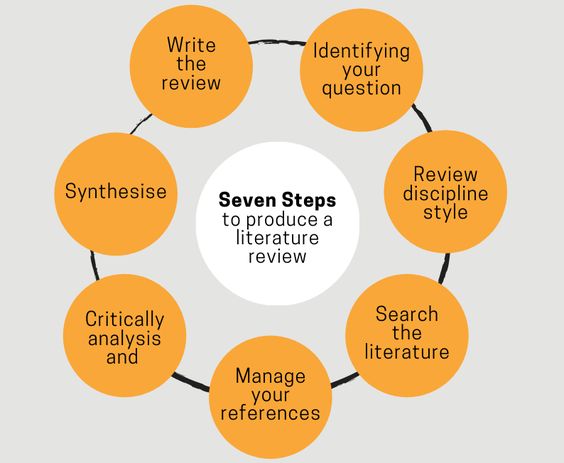
The Process of Writing a Nursing Literature Review
Writing a nursing literature review is a journey of discovery that requires time, effort, and meticulous attention to detail. Follow these steps to navigate the process effectively:
- Develop a Research Question: Formulate a clear and focused research question that guides your search and analysis.
- Conduct a Literature Search: Identify relevant databases, search terms, and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Execute your search strategy and document your process.
- Critically Evaluate the Literature: Assess the quality and relevance of each study, considering methodological rigor, sample size, and potential biases.
- Synthesize the Findings: Group the studies thematically or chronologically, identifying trends, gaps, and inconsistencies.
- Write and Revise: Draft your review, using clear and concise language, and cite all sources accurately. Revise your work multiple times, ensuring coherence, clarity, and accuracy.
- Seek Feedback: Share your review with peers, mentors, or professors for feedback on content, structure, and clarity.
The Importance of Writing Literature Reviews
Writing a nursing literature review is a valuable undertaking that can contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge and practice. Engaging in the critical process of reviewing, analyzing, and synthesizing existing research deepens your understanding of a chosen topic. It also contributes to the growing body of evidence that informs nursing care. Besides, crafting literature reviews also sharpens your writing skills, critical to success in nursing education and practice.
Get the Best Nursing Literature Review Writing Service
Nursingpapers offers professional nursing literature review writing services for undergraduate, degree, Master’s and PhD. We have highly skilled writers to deliver customized academic writing solutions for literature reviews, essays and dissertations at your convenience.