Table of Contents
Nursing is a profession built on a foundation of critical thinking, clinical judgment, and evidence-based practice. A crucial component of developing these essential skills is the meticulous analysis of patient cases. The nursing case study analysis is a powerful tool that allows nursing students and professionals to dissect complex patient situations, identify key issues, and formulate effective care plans.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to write a compelling and insightful nursing case study analysis, ensuring you master this vital skill.
Understanding the Purpose of a Nursing Case Study Analysis
The primary purpose of a nursing case study analysis is not simply to recount a patient’s story, but rather to critically evaluate the care provided, identify areas for improvement, and enhance understanding of nursing principles and best practices. Through a thorough nursing case study analysis, you demonstrate your ability to:
- Apply theoretical knowledge: Integrate classroom learning with real-world patient scenarios.
- Develop critical thinking skills: Analyze complex data, identify patterns, and draw logical conclusions.
- Improve clinical judgment: Evaluate the effectiveness of nursing interventions and identify potential risks.
- Enhance problem-solving abilities: Develop strategies for managing complex patient conditions.
- Promote evidence-based practice: Utilize research and best practices to inform care decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Clearly and concisely communicate your analysis and recommendations.
A well-structured nursing case study analysis showcases your analytical prowess and ability to translate theoretical concepts into practical application. It’s a valuable learning tool that strengthens your foundation as a nurse.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Nursing Case Study Analysis
I. Selecting and Preparing Your Case Study
The selection of an appropriate case study is crucial for a successful nursing case study analysis. Choose a case that is both challenging and relevant, allowing for in-depth analysis and application of your knowledge. Consider factors such as:
- Complexity: The case should present multiple issues and require critical thinking to resolve.
- Relevance: The case should relate to areas you have studied and are familiar with.
- Data Availability: Ensure sufficient data is available to support your analysis.
- Ethical Considerations: Protect patient confidentiality by anonymizing all identifying information.
Once you have selected your case, meticulously gather all relevant data, including:
- Patient demographics: Age, gender, medical history, social history.
- Presenting complaint: The reason for admission or seeking care.
- Physical assessment findings: Vital signs, physical examination results, lab reports.
- Diagnosis: The patient’s medical diagnosis or diagnoses.
- Treatment plan: Medications, therapies, and interventions implemented.
- Nursing interventions: Specific actions taken by nurses to address patient needs.
- Patient outcomes: The results of the implemented care plan.
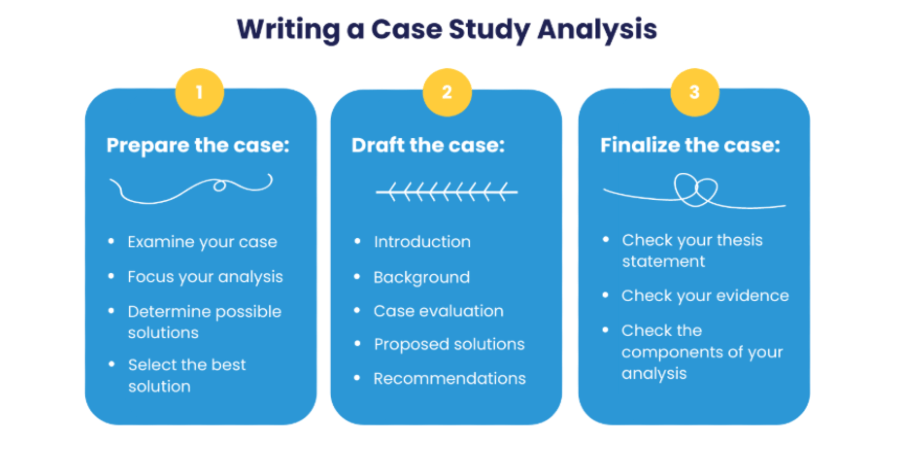
II. Structuring Your Nursing Case Study Analysis
A well-structured nursing case study analysis follows a logical flow, ensuring clarity and coherence. A common structure includes:
- Introduction: Briefly introduce the patient, the context of the case study, and the purpose of your analysis. State your main argument or thesis statement regarding the case.
- Patient Profile: Provide a concise overview of the patient’s demographics, medical history, and presenting complaint.
- Assessment: Detail the patient’s physical assessment findings, including vital signs, lab results, and diagnostic imaging. Analyze this data to identify key issues and potential problems.
- Diagnosis: Identify the relevant nursing diagnoses based on the assessment data. Use the NANDA-I taxonomy for standardized terminology. This section is crucial for a strong nursing case study analysis.
- Planning: Outline the nursing care plan, detailing specific interventions designed to address the identified nursing diagnoses. Justify your chosen interventions using evidence-based practice. This involves citing relevant literature and research to support your plan of care.
- Implementation: Describe the actual nursing interventions implemented. Explain the rationale behind each intervention and document any challenges encountered during implementation.
- Evaluation: Analyze the effectiveness of the interventions implemented. Assess whether the patient’s condition improved, deteriorated, or remained stable. Did the interventions achieve their intended goals? This section is key to a successful nursing case study analysis.
- Conclusion: Summarize your findings and provide overall reflections on the case. Identify areas for improvement in the care provided and suggest recommendations for future practice. Discuss any learning points gained from the experience.
- References: List all sources cited in your nursing case study analysis using a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
III. Writing Your Nursing Case Study Analysis
Writing a strong nursing case study analysis requires clear, concise, and objective language. Avoid subjective opinions and instead focus on factual information supported by evidence. Pay close attention to:
- Accuracy: Ensure all information is accurate and reflects the patient’s actual condition.
- Objectivity: Avoid personal biases and maintain a neutral perspective.
- Clarity: Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may not be understood by the reader.
- Organization: Follow a logical structure and ensure a smooth flow of information.
- Evidence-based practice: Support your analysis and recommendations with evidence from reputable sources.
IV. Critical Analysis and Reflection in your Nursing Case Study Analysis
A successful nursing case study analysis goes beyond simply summarizing the patient’s experience. It involves critical analysis and reflection on the following aspects:
- Strengths and Weaknesses of the Care Provided: Identify areas where the care was effective and areas where it could have been improved.
- Ethical Considerations: Analyze the ethical implications of the case, including patient autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice.
- Interprofessional Collaboration: Discuss the roles of different healthcare professionals in the patient’s care and how they collaborated effectively (or ineffectively).
- Lessons Learned: Reflect on what you learned from the case study and how it has impacted your clinical reasoning and decision-making skills.

V. Review and Editing
Once you have completed your nursing case study analysis, take the time to thoroughly review and edit your work. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and clarity of expression. Ensure that your analysis is well-organized, logical, and supported by evidence. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to identify areas for improvement before submitting your final draft. A well-polished nursing case study analysis demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in a Nursing Case Study Analysis
Nursing case study analysis is a crucial component of nursing education and professional development. It allows students and practicing nurses to critically examine patient situations, apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, and improve their clinical reasoning skills. However, many students and professionals make common mistakes that undermine the learning process and the quality of their analysis. The following are the prevalent errors and practical strategies to avoid them.
1. Insufficient Data Gathering and Review: A fundamental error in nursing case study analysis is failing to gather and thoroughly review all relevant patient data. This includes the patient’s medical history, physical assessment findings, laboratory results, medication list, and progress notes. Incomplete data leads to inaccurate conclusions and a superficial analysis.
- How to avoid it: Develop a systematic approach to data collection. Use a checklist to ensure all relevant information is obtained. Carefully review all documentation, paying attention to details that might seem insignificant at first glance. Don’t hesitate to seek clarification from preceptors or colleagues if information is unclear or missing.
2. Lack of Critical Thinking and Analysis: Simply summarizing the patient’s case is insufficient for a robust nursing case study analysis. The analysis demands critical thinking, interpreting data, identifying patterns, and drawing logical conclusions. A lack of critical analysis results in a descriptive rather than analytical piece.
- How to avoid it: Practice applying the nursing process (assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, evaluation) to the case study. Question the information, identify inconsistencies, explore alternative explanations, and formulate evidence-based nursing diagnoses. Utilize frameworks like the PES (Problem, Etiology, Symptoms) format to organize your thinking and clarify your analysis.
3. Neglecting the Nursing Process: The nursing process is the cornerstone of nursing practice, and its application is essential in any nursing case study analysis. Ignoring this structured approach leads to disjointed and ineffective analysis. The omission of any stage weakens the overall strength of the analysis.
- How to avoid it: Explicitly outline each step of the nursing process in your analysis. Clearly identify the patient’s nursing diagnoses, establish realistic and measurable goals, detail appropriate nursing interventions, and evaluate the effectiveness of your proposed care plan. This structured approach makes your nursing case study analysis more comprehensive and coherent.
4. Failure to Prioritize and Focus: Many nursing case studies present complex scenarios with numerous patient problems. Failing to prioritize these issues and focus on the most critical ones leads to a diffuse and unconvincing analysis.
- How to avoid it: Use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs or other prioritization frameworks to identify the most urgent and life-threatening issues. Focus your analysis on these critical aspects, acknowledging other issues but dedicating the majority of your attention to the most significant problems. This ensures a concise and focused nursing case study analysis.
5. Weak or Missing Evidence-Based Rationale: Assertions made in a nursing case study analysis must be supported by evidence-based literature. Lack of supporting evidence weakens the credibility and persuasiveness of your arguments.
- How to avoid it: Cite relevant nursing literature, research studies, and clinical guidelines to support all your assessments, diagnoses, and interventions. Use reputable sources and accurately reference your findings to demonstrate a solid understanding of evidence-based practice. This enhances the quality and authority of your nursing case study analysis.
6. Poor Organization and Presentation: A poorly organized and presented nursing case study analysis, regardless of its content, is difficult to follow and understand. Poor grammar, inconsistent formatting, and a lack of clarity impede the reader’s comprehension.
- How to avoid it: Structure your analysis logically, using headings and subheadings to guide the reader. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon and technical terms unless necessary. Proofread carefully to eliminate grammatical errors and typographical mistakes. A well-organized and presented nursing case study analysis greatly enhances its impact.
7. Ignoring the Patient’s Perspective: A comprehensive nursing case study analysis considers not only the physiological and medical aspects but also the patient’s subjective experience, psychosocial factors, and cultural background. Ignoring the patient’s perspective results in an incomplete and potentially insensitive analysis.
- How to avoid it: Actively consider the patient’s personal values, beliefs, and preferences when formulating your care plan. Explore the impact of the illness on the patient’s daily life, emotional well-being, and relationships. This holistic approach improves the quality and relevance of your nursing case study analysis.
Mastering the art of nursing case study analysis requires practice, dedication, and a commitment to critical thinking. By avoiding these common mistakes and employing the strategies outlined above, students and practicing nurses can significantly improve the quality of their analyses, enhancing their learning and contributing to better patient care. The depth and thoroughness of a well-executed nursing case study analysis are essential for professional growth and improved clinical outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Case Study Analysis
Nursing case study analysis is a crucial component of nursing education and professional development. It allows students and practitioners to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, honing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. However, many find the process challenging, leading to several recurring questions. The following are the frequently asked questions to demystify the process of nursing case study analysis.
Q1: What exactly is a nursing case study analysis?
A nursing case study analysis involves a detailed examination of a patient’s situation, including their medical history, presenting symptoms, diagnostic findings, treatment plan, and response to care. It’s more than just summarizing the patient’s chart; it requires critical analysis of the information to identify key issues, formulate nursing diagnoses, and propose effective interventions. The goal is to demonstrate an understanding of nursing principles and their application in practice. It often involves evaluating the effectiveness of care provided and suggesting improvements.
Q2: How do I approach a nursing case study analysis? A structured approach is needed, right?
Absolutely! A structured approach is essential for a successful nursing case study analysis. A typical approach involves these steps:
- Data Collection and Organization: Thoroughly review all available information, including the patient’s medical history, physical assessment findings, laboratory results, and progress notes. Organize this data systematically, perhaps using a table or flowchart.
- Identification of Key Issues: Identify the primary and secondary health problems the patient is facing. This often involves analyzing the patient’s symptoms, risk factors, and potential complications.
- Formulation of Nursing Diagnoses: Based on the identified issues, formulate appropriate nursing diagnoses using the NANDA-I (North American Nursing Diagnosis Association International) standardized terminology. Clearly state the problem, etiology, and defining characteristics for each diagnosis.
- Planning and Implementation of Interventions: Develop a plan of care that includes specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Outline appropriate nursing interventions aimed at addressing each nursing diagnosis. Justify your choices based on evidence-based practice.
- Evaluation of Outcomes: Assess the effectiveness of the implemented interventions by evaluating the patient’s response to care. Did the interventions achieve the stated goals? If not, why? This step is crucial for reflecting on your approach and identifying areas for improvement.
- Reflection and Learning: Reflect on the entire process. What did you learn from this case? What were your strengths and weaknesses? How could you improve your approach in future analyses?
Q3: What are some common mistakes to avoid in a nursing case study analysis?
Common pitfalls include:
- Lack of Critical Analysis: Simply summarizing the patient’s chart without critical evaluation.
- Insufficient Justification: Failing to provide evidence-based rationale for chosen interventions.
- Overlooking Relevant Information: Missing crucial details that could significantly impact the analysis.
- Poor Organization and Presentation: Submitting a disorganized and poorly written analysis.
- Failure to Address Ethical Considerations: Neglecting to consider the ethical implications of the patient’s care.
Avoiding these mistakes requires careful planning, thorough data analysis, and a clear understanding of nursing principles.
Q4: How can I improve my skills in performing a nursing case study analysis?
Improving your skills involves practice and active learning. Consider these strategies:
- Practice Regularly: Work through numerous case studies, gradually increasing the complexity of the scenarios.
- Seek Feedback: Ask instructors or experienced nurses to review your analyses and provide constructive criticism.
- Utilize Resources: Consult nursing textbooks, journals, and online databases to access relevant information and evidence-based practices.
- Engage in Group Discussions: Discuss case studies with peers to learn from different perspectives and enhance your understanding.
- Focus on the Nursing Process: Mastering the nursing process (assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, evaluation) is fundamental to successful nursing case study analysis.
Q5: How is a nursing case study analysis different from a medical case study analysis?
While both involve analyzing patient cases, a nursing case study analysis focuses specifically on the nursing care aspects. This includes the nursing diagnoses, interventions, and evaluation of nursing outcomes. Medical case studies, on the other hand, often concentrate on the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions from a physician’s perspective. Nurses might be involved in gathering medical data, but the focus of the nursing case study analysis will be the patient’s holistic needs and the nursing care provided to meet these needs. Understanding this distinction is key to producing a strong and focused analysis.

Nursing case study analysis writing requires a systematic approach, critical thinking, and a solid understanding of nursing principles. By following the steps outlined above and addressing potential pitfalls, students and professionals can effectively utilize this valuable tool to enhance their knowledge, skills, and overall competence in nursing practice.
Writing a strong nursing case study analysis needs careful planning, meticulous data gathering, critical analysis, and clear communication. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can develop the skills necessary to produce a compelling and insightful analysis that enhances your understanding of nursing principles and best practices, ultimately leading to improved patient care. The nursing case study analysis is a vital tool for your professional development and should be approached with diligence and attention to detail. Mastering this skill will significantly benefit your future career in nursing.
Get Professional Nursing Case Study Writing Service
At Nursing Papers, we can assist you to write original and impactful nursing case study analysis. Our service covers topic suggestion, case study writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Apart from nursing case studies, we can also help you to write top-notch research papers, essays and dissertations.