Table of Contents
Nursing research is a critical component of the profession, driving improvements in patient care, advancing the science of nursing practice, and shaping healthcare policies. It empowers nurses to actively contribute to the body of knowledge that informs their work and ensures the delivery of optimal care. However, embarking on a research journey can feel daunting, especially for novice researchers.
This article will serve as a comprehensive guide, outlining essential steps for navigating the intricate process of successful nursing research.
Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Nursing Research
1. Defining a Clear Research Question:
The cornerstone of any successful nursing research project lies in the formulation of a well-defined research question. This question acts as the guiding star, directing the entire research process. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
a) Start with an Area of Interest: Identify a gap in current knowledge or a problem that needs addressing within your field of practice. This could be anything from understanding the effectiveness of a new intervention to exploring patient experiences with a particular condition.
b) Formulate a Specific Question: Instead of asking broad questions like “How can we improve patient satisfaction?”, frame your research question more specifically, such as “What is the impact of implementing a patient-centered communication strategy on patient satisfaction in the emergency department?”
c) Ensure Feasibility: Consider your resources, including time, funding, and access to data. A well-defined research question will guide your entire research process and contribute to the overall success of your nursing research project.
2. Conducting a Thorough Literature Review:
A thorough literature review is essential to inform your nursing research project. It provides context for your study, highlights existing knowledge, identifies gaps in the literature, and helps refine your research question.
a) Identify Relevant Keywords: Choose keywords that accurately reflect your research question and area of interest. This will help you locate relevant publications.
b) Utilize Multiple Databases: Explore various databases, such as CINAHL, PubMed, PhD Nurse Writer and Scopus, to access a comprehensive range of research articles related to your topic.
c) Analyze and Synthesize Information: Critically evaluate the research findings and identify common themes, conflicting results, and unanswered questions. This analysis will help you formulate your research hypothesis and design your study.
3. Developing a Robust Research Design:
The research design is the blueprint for your nursing research project, outlining the methods you will use to collect and analyze data. Choosing the appropriate design is crucial for achieving valid and reliable results.
a) Quantitative vs. Qualitative: Quantitative research focuses on measuring and quantifying phenomena using numerical data, while qualitative research explores the experiences and perspectives of individuals using descriptive and interpretive methods.
b) Experimental vs. Non-Experimental: Experimental designs involve manipulating variables to observe cause-and-effect relationships, while non-experimental designs examine existing relationships or describe phenomena without manipulation.
c) Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal: Cross-sectional studies collect data at a single point in time, while longitudinal studies track changes over time.
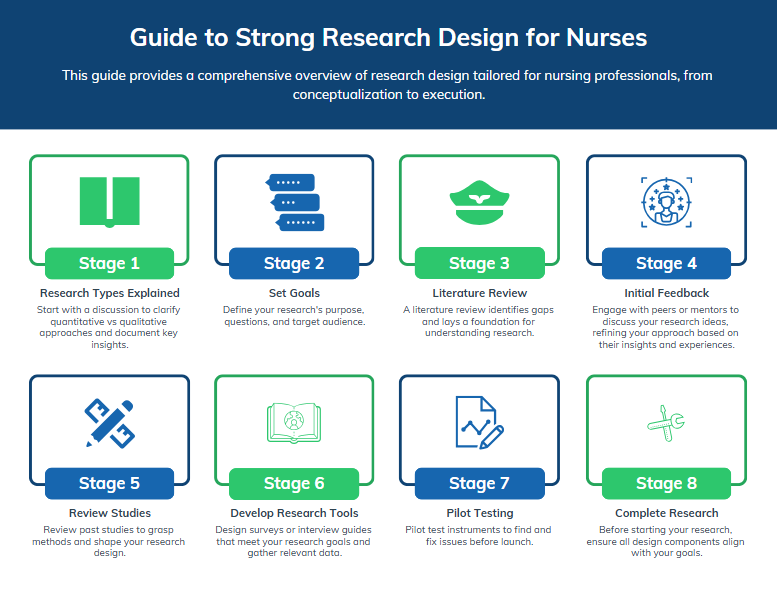
4. Ensuring Ethical Considerations:
Ethical considerations are paramount in nursing research. Research must be conducted ethically and with respect for the participants, ensuring their safety and well-being.
a) Informed Consent: All participants must be informed about the research objectives, procedures, risks, and benefits before providing informed consent.
b) Confidentiality and Anonymity: Participant data must be protected through appropriate measures to ensure confidentiality and anonymity.
c) Institutional Review Board (IRB) Approval: All nursing research projects involving human subjects require approval from an IRB, which ensures the ethical and scientific rigor of the study.
5. Collecting and Analyzing Data:
Data collection is a crucial step in nursing research. The methods used will depend on the research design and the specific question being investigated.
a) Qualitative Data Collection: Methods include interviews, focus groups, observations, and document analysis.
b) Quantitative Data Collection: Methods include surveys, questionnaires, physiological measurements, and existing databases.
c) Data Analysis: Qualitative data is analyzed using thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Quantitative data is analyzed using statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and hypothesis testing.
6. Interpreting and Communicating Findings:
After collecting and analyzing data, the next step is to interpret the findings and communicate them effectively to the broader nursing community.
a) Drawing Meaningful Conclusions: Analyze the data and draw logical conclusions based on the evidence.
b) Writing a Research Report: Organize your findings into a clear and concise research report that includes an introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
c) Disseminating Findings: Present your findings at conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, or share with colleagues and practitioners.
7. Utilizing Research Findings:
The ultimate goal of nursing research is to improve patient care and advance the science of nursing practice. The findings from your study can be used to:
a) Enhance Clinical Practice: Implement evidence-based interventions to improve patient outcomes.
b) Inform Policy Decisions: Advocate for changes in healthcare policies based on the research evidence.
c) Foster Professional Growth: Share your findings with colleagues and contribute to the continuous learning and development of the nursing profession.
Challenges and Opportunities in Nursing Research
While nursing research offers immense potential to transform patient care and advance the profession, it faces certain challenges:
a) Funding Constraints: Securing adequate funding for research projects can be difficult, particularly for smaller studies or pilot projects.
b) Time Constraints: Nurses often juggle multiple responsibilities, making it challenging to dedicate sufficient time to research.
c) Lack of Research Skills: Not all nurses have the necessary research skills and training to conduct robust studies.
Despite these challenges, nursing research holds significant promise for the future of nursing. Here are some key opportunities:
a) Integration of Technology: Advances in technology, such as electronic health records and mobile health applications, offer new opportunities for data collection, analysis, and dissemination of nursing research findings.
b) Interprofessional Collaboration: Collaboration between nurses, physicians, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals can enhance the quality and impact of nursing research.
c) Emphasis on Patient-Centered Research: Increasing focus on patient-centered care necessitates research that explores patient experiences, preferences, and outcomes.
The Common Mistakes in Nursing Research and How to Avoid Them
Nursing research plays a crucial role in advancing the field of nursing practice. It informs evidence-based care, improves patient outcomes, and shapes the future of healthcare delivery. However, even the most well-intentioned nursing research can be undermined by common pitfalls. Understanding these mistakes and implementing strategies to avoid them is essential for conducting robust and meaningful research.
1. Lack of Clear Research Question:
A well-defined research question serves as the foundation of any successful study. A vague or poorly formulated question will lead to a research project that lacks direction and clarity. This can result in irrelevant findings and difficulty in interpreting the results.
To avoid this mistake:
- Start with a specific area of interest. Identify a gap in current knowledge within your field of nursing practice.
- Use the PICO format (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) to structure your question. This provides a clear and concise framework for formulating a research question.
- Consult with experts in the field. Get feedback on your research question to ensure it is well-defined and relevant.
2. Inadequate Literature Review:
A thorough literature review is crucial for understanding the existing knowledge base and identifying potential research gaps. Skipping this step can lead to duplication of research and neglecting relevant existing studies.
To avoid this mistake:
- Search multiple databases using relevant keywords and filters.
- Critically evaluate the quality and relevance of the studies included in your review.
- Synthesize the findings from your literature review and identify key themes and areas for further exploration.
3. Poor Study Design and Methodology:
The chosen research design and methodology are vital for ensuring the validity and reliability of your findings. Selecting an inappropriate design or using flawed methodologies can compromise the integrity of your research.
To avoid this mistake:
- Choose a research design that is appropriate for your research question. Consider qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods designs.
- Use established methods for data collection and analysis. Consult with experienced researchers and ensure your methods are aligned with best practices.
- Address potential biases and limitations in your study design. Acknowledge these limitations in your research report.
4. Insufficient Sample Size:
A sufficiently large sample size is crucial for generalizability and statistical power. A small sample size can lead to unreliable results and limit the applicability of your findings.
To avoid this mistake:
- Calculate the required sample size using appropriate statistical formulas or software.
- Consider factors such as the population size, heterogeneity, and desired level of statistical power.
- Recruit a sample that is representative of the target population.
5. Data Collection Errors:
Accurate and reliable data collection is essential for producing valid research findings. Errors in data collection, such as inconsistencies or missing data, can significantly impact the results and lead to inaccurate conclusions.
To avoid this mistake:
- Train data collectors thoroughly and ensure they understand the protocols for data collection.
- Use standardized data collection tools and procedures to minimize variability.
- Regularly check the quality of data collected and implement measures to address any errors.
6. Inadequate Data Analysis:
Analyzing data correctly is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from your research. Incorrect or insufficient data analysis can lead to misleading conclusions and misinterpretation of findings.
To avoid this mistake:
- Select appropriate statistical methods for data analysis based on the research design and data type.
- Utilize statistical software to perform complex data analyses and ensure accuracy.
- Consult with a statistician for assistance with data analysis and interpretation.
7. Insufficient Discussion of Findings:
Interpreting and discussing the findings of your research are essential for providing context and drawing meaningful conclusions. Limited discussion or failure to relate findings to existing literature can weaken the impact of your study.
To avoid this mistake:
- Analyze and interpret your findings in relation to the research question and existing literature.
- Discuss the implications of your findings for nursing practice, education, and research.
- Acknowledge the limitations of your study and suggest potential areas for future research.
8. Neglecting Ethical Considerations:
Nursing research must always adhere to ethical principles, including informed consent, confidentiality, and minimizing risk to participants. Failure to address ethical considerations can have severe consequences for participants and the research project.
To avoid this mistake:
- Obtain ethical approval from an institutional review board (IRB) before conducting any research involving human participants.
- Ensure participants are fully informed about the risks and benefits of participating in the study.
- Protect the confidentiality and privacy of participants’ data.

9. Poor Communication of Findings:
Clear and concise communication of research findings is crucial for disseminating knowledge and influencing practice. Poorly written reports, lack of dissemination, or failure to communicate findings in a relevant format can limit the impact of your work.
To avoid this mistake:
- Prepare a well-structured and informative research report using a clear and concise writing style.
- Disseminate your findings through peer-reviewed publications, conferences, and presentations.
- Tailor your communication to the target audience and use appropriate language and format.
By understanding and avoiding these common mistakes, nurses can conduct high-quality nursing research that contributes to the advancement of the field and improves patient outcomes. By adhering to ethical principles, conducting rigorous research, and effectively communicating findings, nurses can make a significant difference in the lives of their patients and the profession of nursing as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Research
Nursing research plays a vital role in improving patient care, advancing the profession, and shaping healthcare policies. However, the world of research can seem daunting, especially for those new to the field. To demystify the process, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions about nursing research, covering everything from its purpose to its practical applications.
1. What is nursing research?
Nursing research is a systematic and rigorous investigation that seeks to advance knowledge and understanding of nursing practice, patient care, and health outcomes. It involves asking questions, collecting data, analyzing findings, and interpreting the results to inform decision-making and improve patient care. This research can be conducted on a wide range of topics, including:
- Patient safety: Investigating the effectiveness of interventions to prevent hospital-acquired infections or reduce medication errors.
- Nursing interventions: Testing the efficacy of new techniques for pain management, wound care, or promoting patient comfort.
- Health outcomes: Studying the impact of nursing interventions on patient satisfaction, quality of life, and overall health.
- Nursing education: Evaluating the effectiveness of different teaching strategies and their impact on student learning.
- Policy and advocacy: Examining the influence of nursing research on healthcare policy and its contribution to promoting patient rights and access to care.
2. Why is nursing research important?
Nursing research is essential for:
- Improving patient care: By providing evidence-based practices, it helps nurses deliver the best possible care to their patients.
- Advancing the profession: It strengthens the scientific foundation of nursing and establishes its credibility as a profession.
- Influencing healthcare policy: Research findings can inform policymakers on best practices and resource allocation.
- Promoting patient safety: Studies focused on patient safety contribute to reducing medical errors and improving outcomes.
3. How do I get involved in nursing research?
There are many ways to engage in nursing research, regardless of your experience level:
- Participate in a research study: Volunteering as a participant in a research study is a great way to contribute to the field.
- Assist a researcher: Offer to help with data collection, analysis, or literature reviews.
- Join a research team: Many hospitals and universities have research teams that welcome new members.
- Take a course or workshop: Several educational opportunities exist to develop research skills, such as statistics and research methods.
- Read and disseminate research findings: Stay up-to-date with the latest findings by reading research journals and sharing insights with colleagues.
4. What are the different types of nursing research?
Nursing research can be categorized into various types based on the research question and methodology. Some common types include:
- Quantitative research: Focuses on measuring and testing hypotheses using numerical data.
- Qualitative research: Explores subjective experiences and meanings through interviews, observations, and text analysis.
- Mixed methods research: Combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon.
- Clinical research: Investigates the effectiveness of treatments, interventions, and medications in a clinical setting.
- Basic research: Focuses on fundamental principles and theories to advance understanding of nursing practice.
5. How is nursing research funded?
Funding for nursing research comes from various sources, including:
- Government agencies: National Institutes of Health (NIH), Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ).
- Private foundations: Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, American Nurses Foundation.
- Professional organizations: American Nurses Association, Sigma Theta Tau International.
- Hospitals and healthcare systems: Many institutions have internal funding programs to support research.
6. What are some challenges to conducting nursing research?
While nursing research plays a crucial role in advancing the profession, it faces some challenges:
- Funding: Securing adequate funding for research projects can be challenging, especially for smaller-scale studies.
- Time constraints: Nurses often have limited time and resources to dedicate to research due to their clinical responsibilities.
- Access to data: Collecting data from patients and healthcare systems can be complex and require specific ethical considerations.
- Dissemination of findings: Ensuring that research findings are disseminated effectively to practitioners and policymakers can be challenging.
7. Where can I find information about nursing research?
- Professional journals: The American Journal of Nursing, Nursing Research, and Research in Nursing & Health.
- Online databases: PubMed, Nursing Papers, CINAHL, PsycINFO.
- Professional organizations: American Nurses Association, Sigma Theta Tau International.
- University libraries: University libraries offer access to a wide range of research materials.
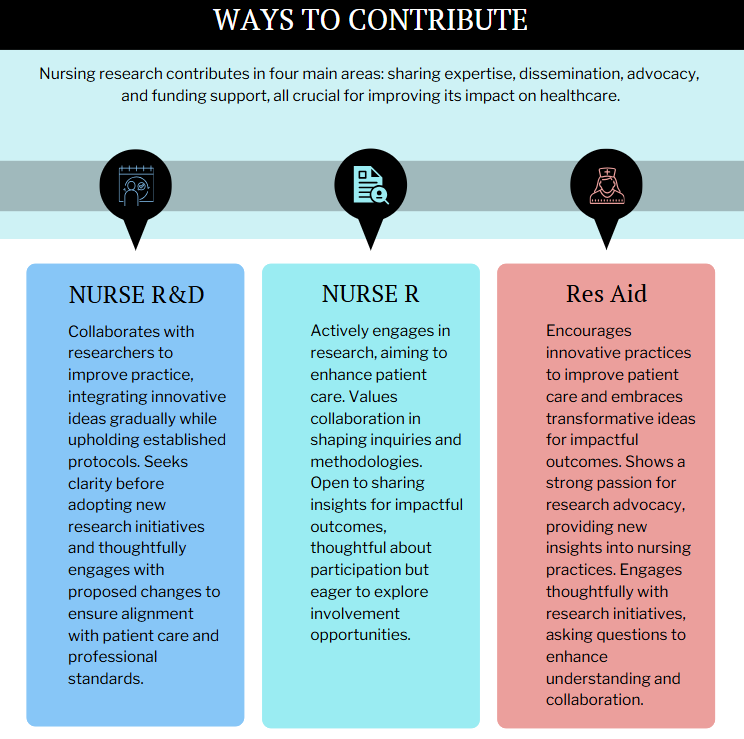
8. How can I contribute to nursing research?
Even if you aren’t directly conducting research, you can contribute to the field in various ways:
- Share your expertise with researchers: Provide insights into clinical practice and patient needs.
- Participate in research dissemination activities: Share research findings with colleagues and contribute to the discussion.
- Advocate for nursing research: Highlight the importance of research to your colleagues, administrators, and policymakers.
- Support research funding: Contribute to organizations that fund nursing research.
Nursing research is a dynamic and evolving field that holds immense potential to improve patient care, advance the profession, and shape healthcare policy. Whether you are a seasoned nurse or just starting your career, there are numerous ways to engage in and contribute to nursing research. By understanding the basics of this field, you can become an active participant in driving positive change in healthcare.
Final Thoughts
Nursing research is a dynamic and essential endeavor that contributes significantly to the advancement of the profession. By adhering to these essential guidelines, nurses can conduct rigorous and impactful nursing research that improves patient care, shapes healthcare policies, and advances the science of nursing practice. From defining a clear research question to effectively disseminating findings, every step in the research process is vital. Embrace the challenges, leverage the opportunities, and embark on the journey of nursing research to make a meaningful contribution to the field.
Get Customized Nursing Research and Paper Writing Service
At Nursing Papers, we offer professional research and paper writing services for nursing courses. We can assist you with choosing compelling topics, writing authentic nursing papers, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Get in touch with us for customized assistance with essays, research papers and dissertations.