Table of Contents
The healthcare landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving patient needs, demographic shifts, and systemic pressures. At the heart of this transformation lies the nursing profession – adaptable, resilient, and indispensable. As we look towards 2025, understanding the key forces shaping nursing practice, education, and policy is crucial for nurses, healthcare leaders, educators, and policymakers alike. Staying abreast of emerging nursing trends allows the profession to proactively adapt, innovate, and continue delivering high-quality, patient-centered care in an increasingly complex environment.
The year 2025 promises to be a pivotal point, consolidating changes accelerated by recent global events while introducing new paradigms of care delivery and professional development. Nurses will find themselves at the intersection of advanced technology and fundamental human compassion, navigating challenges while seizing opportunities to redefine their roles and impact. Examining the trajectory of current developments allows us to anticipate the most significant nursing trends that will define the profession in the near future. These trends encompass a wide spectrum, from the integration of artificial intelligence to a renewed focus on nurse well-being and the expansion of practice scopes.
This article explores the top 10 nursing trends poised to make a significant impact in 2025.
The Top 10 Nursing Trends for 2025 and Beyond
The AI Revolution in Nursing Care and Workflow
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly moving from a futuristic concept to a practical tool within healthcare, and its integration into nursing is one of the most profound nursing trends we anticipate for 2025. AI’s potential spans across various nursing functions, aiming to enhance efficiency, improve clinical decision-making, and personalize patient care.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets (EHRs, vital signs, genomics) to predict patient deterioration, identify individuals at high risk for specific conditions (like sepsis or falls), and forecast potential staffing needs. This allows nurses to intervene proactively, potentially improving patient outcomes and resource allocation.
- Workflow Automation: Mundane and time-consuming tasks, such as documentation, scheduling, and inventory management, can be increasingly automated by AI-powered tools. This frees up valuable nursing time, allowing nurses to focus on direct patient care, critical thinking, and complex human interactions – aspects where their skills are irreplaceable.
- Clinical Decision Support: AI can provide nurses with real-time, evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. This might include suggesting appropriate interventions based on patient data, flagging potential drug interactions, or providing summaries of complex patient histories. This specific nursing trend supports safer and more informed practice.
- Personalized Patient Education: AI can tailor patient education materials based on individual learning styles, health literacy levels, and specific conditions, enhancing patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
While the potential is immense, the integration of AI also presents challenges, including ethical considerations (bias in algorithms, data privacy), the need for adequate training, and ensuring that technology complements, rather than replaces, the essential human element of nursing. Navigating this integration thoughtfully is a key aspect of contemporary nursing trends.
Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Ascendancy
The adoption of telehealth surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, but its continued growth and integration into routine care represent one of the defining nursing trends for 2025 and beyond. Telehealth, encompassing virtual visits, remote monitoring, and mobile health applications, is fundamentally changing how and where nursing care is delivered.
- Expanded Access: Telehealth bridges geographical barriers, providing access to nursing expertise for patients in rural or underserved areas, as well as those with mobility limitations.
- Chronic Disease Management: RPM technologies (wearable sensors, connected devices) allow nurses to continuously monitor patients with chronic conditions (e.g., heart failure, diabetes, COPD) from their homes. Nurses can track vital signs, symptoms, and adherence, intervening early to prevent exacerbations and hospital readmissions. This proactive approach is a hallmark of evolving nursing trends.
- Specialized Consultations: Telehealth facilitates access to specialist nurses (e.g., wound care, oncology, mental health) for consultations, improving the quality of care without requiring patient travel.
- Triage and Follow-up: Virtual platforms are increasingly used for initial patient triage, post-discharge follow-up, and medication management, optimizing healthcare resource utilization.

Nurses are central to the success of telehealth, requiring new skill sets in virtual communication, technology management, and interpreting remote data. Ensuring equitable access (addressing the digital divide), maintaining patient privacy, and adapting licensing and reimbursement policies across state lines remain ongoing considerations within this significant nursing trend.
Heightened Focus on Nurse Well-being, Mental Health, and Resilience
The immense pressures faced by the nursing workforce, exacerbated by the pandemic but rooted in long-standing systemic issues, have brought nurse well-being to the forefront. Addressing burnout, moral distress, and mental health challenges is not just an ethical imperative but a critical strategy for workforce retention and patient safety. This focus represents one of the most urgent nursing trends for 2025.
- Systemic Solutions: Healthcare organizations are increasingly recognizing that well-being is not solely an individual responsibility. They are implementing systemic changes, such as:
- Improved staffing ratios and workload management.
- Creating supportive and psychologically safe work environments.
- Promoting cultures that destigmatize seeking mental health support.
- Offering easily accessible mental health resources (counseling, peer support programs, mindfulness training).
- Technology for Support: Apps and platforms dedicated to mental wellness, stress management, and resilience building are becoming more common tools offered to nursing staff.
- Leadership Training: Equipping nurse leaders with the skills to recognize signs of distress in their teams and foster supportive environments is becoming a priority.
- Policy Advocacy: Professional nursing organizations are advocating for policies that support safe staffing levels, protect nurses from workplace violence, and ensure adequate resources for mental health services.
Sustaining the nursing workforce requires a fundamental shift towards prioritizing the health and well-being of nurses themselves. This people-centric nursing trend is essential for the future health of the entire healthcare system. Ignoring these crucial nursing trends related to workforce health could have dire consequences.
Expansion of Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) Scope of Practice
As healthcare systems grapple with physician shortages and the need for accessible, cost-effective care, the role of Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs) – including Nurse Practitioners (NPs), Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs), Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs), and Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs) – continues to expand. Granting APRNs full practice authority (FPA) is a significant legislative and professional nursing trend.
- Full Practice Authority: More states are moving towards FPA, allowing APRNs to evaluate patients, diagnose, order and interpret diagnostic tests, initiate and manage treatments—including prescribing medications—under the exclusive licensure authority of the state board of nursing.
- Primary Care Providers: NPs, in particular, are playing an increasingly vital role in delivering primary care, especially in underserved rural and urban areas, helping to alleviate access issues.
- Specialized Roles: APRNs are filling critical gaps in specialized areas like gerontology, psychiatric mental health, pediatrics, and acute care.
- Leadership and Policy Influence: With expanded roles comes increased influence in healthcare leadership, policy development, and system redesign.
This nursing trend underscores the high level of education, skill, and autonomy possessed by APRNs. Ongoing advocacy efforts aim to standardize scope of practice laws across all states, removing barriers that limit APRNs from practicing to the full extent of their education and training. This is one of the nursing trends with major policy implications.
Deepening Emphasis on Health Equity and Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)
There is growing recognition within healthcare that clinical care alone cannot achieve optimal health outcomes. Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) – the conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age – have a profound impact on health risks and outcomes. Addressing health equity and integrating SDOH into nursing practice is one of the most critical nursing trends for 2025.
- Screening and Assessment: Nurses are increasingly incorporating SDOH screening tools into routine patient assessments to identify non-medical factors (e.g., food insecurity, housing instability, lack of transportation, limited health literacy) affecting health.
- Community Partnerships: Nurses are collaborating more closely with community-based organizations, social services, and public health agencies to connect patients with necessary resources.
- Culturally Competent Care: Enhanced focus on providing care that is sensitive to diverse cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and values is crucial for building trust and improving outcomes across different populations. This includes ongoing education in cultural humility for nursing staff.
- Advocacy for Policy Change: Nurses are leveraging their trusted position to advocate for policies that address systemic inequities and improve social conditions that impact health (e.g., affordable housing, access to nutritious food, safe environments).
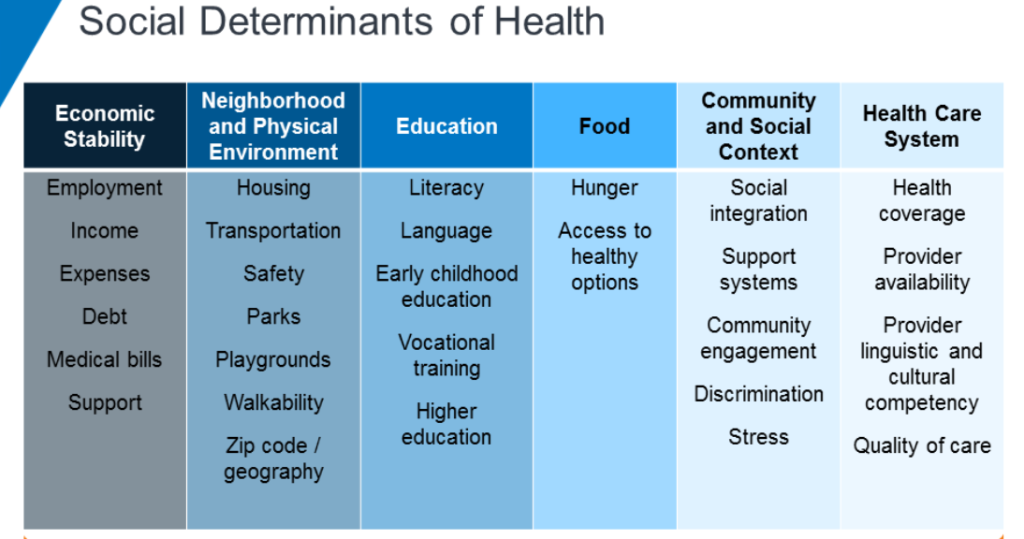
This nursing trend requires nurses to broaden their perspective beyond the clinical setting and engage with the complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors influencing patient well-being. Understanding these broader nursing trends helps create a more holistic approach to care.
Personalized Medicine and Genomics Integration into Nursing Practice
Advances in genomics and our understanding of individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle are paving the way for personalized medicine – tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. Integrating genomics into nursing practice is an emerging but important nursing trend.
- Genomic Literacy: Nurses will need a foundational understanding of genomics to effectively care for patients undergoing genetic testing, receiving targeted therapies, or participating in genomic research. This includes understanding inheritance patterns, implications of genetic test results, and ethical considerations.
- Patient Education and Counseling: Nurses play a vital role in educating patients and families about genetic concepts, the purpose and potential outcomes of genetic testing, and the implications for their health and treatment options.
- Administering Targeted Therapies: Many new treatments, particularly in oncology, are targeted based on a patient’s specific genetic mutations. Nurses are responsible for administering these therapies safely and monitoring for unique side effects.
- Ethical, Legal, and Social Implications (ELSI): Nurses must be prepared to navigate the complex ELSI associated with genomic information, including privacy, potential for discrimination, and equitable access to testing and treatments.
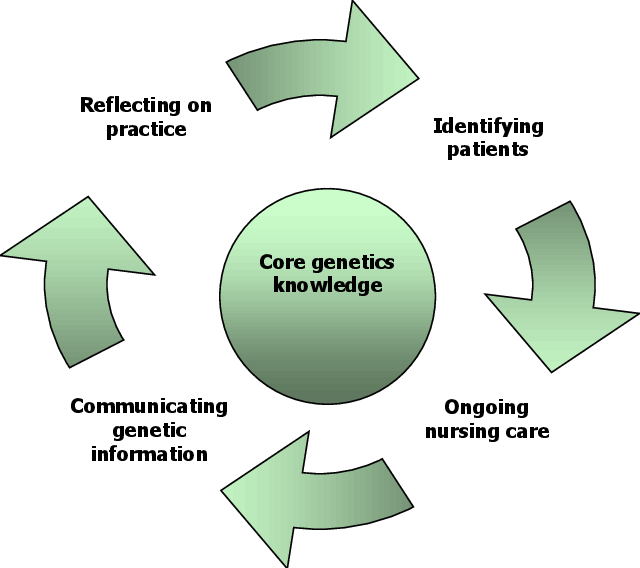
While specialized genetic counselors exist, all nurses will increasingly encounter genomics in their practice. Educational programs and continuing education are adapting to incorporate this essential knowledge, reflecting its growing importance among nursing trends.
The Rise of Specialized and Niche Nursing Roles
As healthcare becomes more complex and specialized, the demand for nurses with advanced expertise in specific areas continues to grow. Beyond traditional hospital units, specialized nursing roles are flourishing, representing a significant nursing trend focused on depth of knowledge.
- Informatics Nurse Specialist: Bridges the gap between clinical practice and information technology, optimizing EHRs, analyzing data, and implementing new technologies.
- Forensic Nurse: Provides specialized care for victims of trauma and violence, collects evidence, and may testify in court.
- Nurse Navigator: Guides patients through complex healthcare systems, coordinating care, connecting them with resources, and providing education and support, often for specific conditions like cancer or chronic diseases.
- Legal Nurse Consultant: Uses clinical expertise to consult on medical-related legal cases.
- Tele-ICU Nurse: Provides remote monitoring and support for critically ill patients in multiple ICUs from a central command center.
- Public Health Nurse: Focuses on population health, disease prevention, and health promotion within communities.
This diversification offers nurses numerous career pathways and opportunities for professional growth. It also highlights the need for specialized training and certification programs to validate expertise. These specialized roles are a direct result of evolving healthcare needs and are key nursing trends shaping career trajectories.
Flexible Staffing Models and the “Gig Economy” in Nursing
Traditional staffing models are being challenged by nurse preferences for greater flexibility and work-life balance, alongside organizational needs for adaptable staffing solutions. The rise of the “gig economy” concept within nursing is an increasingly visible nursing trend.
- Internal Agency Models: Hospitals are creating their own internal float pools or resource teams, offering premium pay and flexibility to nurses who work across different units, reducing reliance on expensive external agencies.
- Technology Platforms: Online platforms and apps are connecting nurses directly with healthcare facilities for per diem shifts or short-term contracts, allowing nurses to choose when and where they work.
- Shared Governance in Scheduling: Models that give nurses more input and control over their schedules are gaining traction, improving job satisfaction and retention.
- Remote Nursing Roles: The growth of telehealth and virtual care creates opportunities for nurses seeking remote work arrangements.
While offering flexibility, this nursing trend also raises questions about benefits, job security, continuity of care, and maintaining team cohesion. Healthcare organizations must find ways to balance flexibility with stability and ensure consistent quality of care. The evolution of staffing is one of the most dynamic nursing trends impacting daily operations.
Enhanced Interprofessional Collaboration and Team-Based Care
The complexity of modern healthcare demands a collaborative approach. Breaking down traditional silos and fostering effective teamwork among nurses, physicians, pharmacists, therapists, social workers, and other health professionals is crucial for patient safety and optimal outcomes. Enhanced interprofessional collaboration is a fundamental nursing trend.
- Shared Care Plans: Teams work together to develop, implement, and evaluate integrated care plans centered around the patient’s goals.
- Interprofessional Rounds: Structured team rounds where all relevant disciplines contribute to discussion and decision-making regarding patient care.
- Communication Technologies: Utilizing shared electronic health records and secure communication platforms to facilitate seamless information exchange among team members.
- Interprofessional Education (IPE): Integrating IPE into health professions curricula to prepare future clinicians for collaborative practice from the outset of their careers.
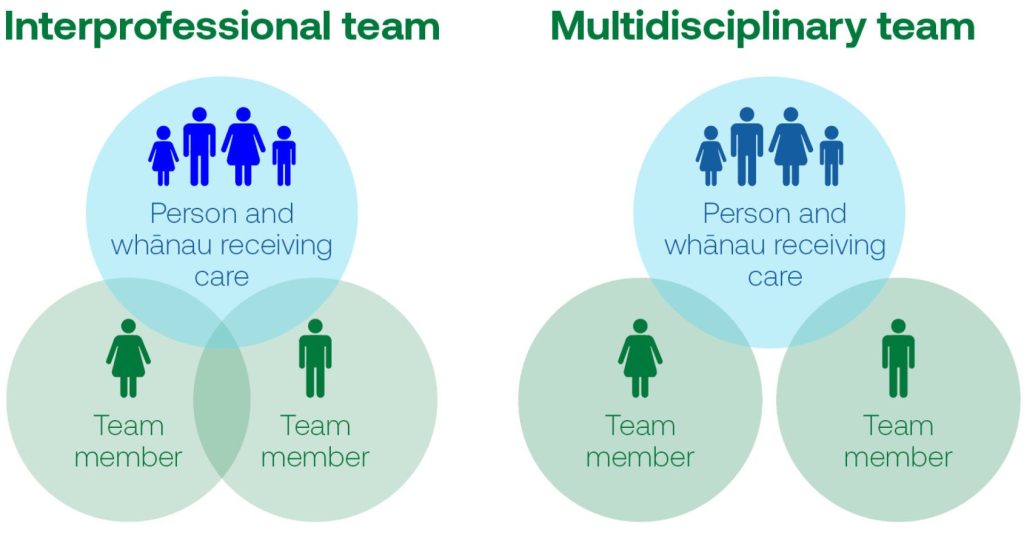
Nurses, often serving as care coordinators and possessing a holistic view of the patient, are pivotal in driving effective interprofessional collaboration. This nursing trend emphasizes communication, mutual respect, and a shared understanding of roles and responsibilities within the healthcare team. It’s one of the foundational nursing trends for improving quality.
The Lifelong Learning and Upskilling Imperative
Given the rapid pace of change in healthcare, technology, and clinical knowledge, the need for continuous professional development and lifelong learning has never been more critical for nurses. This commitment to ongoing education is a defining nursing trend.
- Adapting to Technology: Nurses need continuous training to effectively utilize new technologies like AI, advanced EHR functionalities, telehealth platforms, and RPM devices.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Staying current with the latest research findings and integrating evidence into practice requires ongoing learning and critical appraisal skills.
- Specialization and Certification: Pursuing advanced degrees, certifications, and micro-credentials allows nurses to deepen their expertise and advance their careers in line with emerging nursing trends.
- Reskilling for New Roles: As healthcare models evolve, nurses may need to acquire new skills for roles in areas like data analytics, population health management, or virtual care coordination.
- Mandatory Continuing Education: Regulatory bodies continue to emphasize and often mandate continuing education to ensure competency and patient safety.
Healthcare organizations and educational institutions must provide accessible, relevant, and flexible learning opportunities. Nurses themselves must embrace a mindset of continuous learning to remain competent, adaptable, and effective throughout their careers. Keeping up with these nursing trends requires dedication.
Navigating the Educational and Research Landscape
Understanding these dynamic nursing trends is not just for practicing clinicians; it’s equally vital for nursing students, educators, and researchers. Curricula must adapt to incorporate topics like AI, telehealth, genomics, SDOH, and interprofessional education. Research is needed to evaluate the impact of these trends, identify best practices, and address emerging challenges.
Students and researchers often explore these emerging nursing trends, seeking to understand their implications for practice, policy, and patient outcomes. The complexity of topics like AI ethics in nursing, the effectiveness of different telehealth interventions, or the impact of FPA for APRNs requires rigorous investigation. Sometimes, navigating the demands of academic work while staying current can be challenging. Students might seek resources like nursing paper writing services for assistance in structuring complex arguments or managing heavy coursework.
Others might specifically need help with a nursing research paper to effectively analyze data or synthesize literature related to these cutting-edge nursing trends. At Nursing Papers, we can help you with crafting authentic and impactful essays, research papers, thesis and dissertations about nursing trends. Our services cover topic suggestion, paper writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal.
Conclusion: The Future is Now
The nursing profession in 2025 stands at a fascinating juncture, shaped by powerful technological advancements, pressing workforce demands, and a deepening commitment to holistic, equitable care. The top 10 nursing trends discussed here – from AI integration and telehealth dominance to the critical focus on well-being, expanded APRN roles, and the imperative of lifelong learning – paint a picture of a dynamic and evolving field.
These nursing trends are not isolated phenomena; they are interconnected and often influence one another. Technology impacts workflow and enables new care models; workforce well-being is essential for adopting any new practice effectively; expanded scopes of practice leverage advanced skills; and a focus on equity and SDOH requires new ways of thinking and collaborating.
Navigating these nursing trends successfully will require adaptability, resilience, strong leadership, and a continued commitment to the core values of nursing: compassion, advocacy, and patient-centeredness. Nurses must be prepared to embrace new technologies, acquire new skills, work in increasingly collaborative teams, and advocate for both their patients and their profession. Healthcare organizations, policymakers, and educators have a crucial role to play in supporting nurses through these transitions, providing necessary resources, training, and supportive environments.
While challenges undoubtedly exist, the future of nursing is also ripe with opportunity. These nursing trends highlight pathways for nurses to enhance their impact, improve patient outcomes, increase access to care, and shape a healthier future for all. By understanding and proactively engaging with these pivotal nursing trends, the nursing profession can continue to lead and innovate, ensuring its vital role in the healthcare system of 2025 and beyond. The ongoing evolution of nursing trends underscores the profession’s enduring relevance and adaptability.