Table of Contents
The world of nursing research is vast and complex, with quantitative research playing a crucial role in advancing knowledge and improving patient care. However, crafting a compelling and impactful quantitative nursing research paper requires more than just collecting data and analyzing findings. It demands a systematic and rigorous approach, weaving together theoretical frameworks, robust methodology, and clear communication of results.
This article aims to equip aspiring researchers with a comprehensive guide to writing an outstanding quantitative nursing research paper, offering strategies and insights to navigate the labyrinth of research and emerge with a paper that stands out from the crowd.
What is a Quantitative Research Paper?
A quantitative nursing research paper is a type of academic writing that uses numerical data to explore and analyze a specific topic. It’s characterized by:
1. Objective Approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and unbiased, focusing on measurable facts and figures rather than subjective interpretations.
2. Numerical Data: The core of the paper is the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis of existing data.
3. Hypothesis Testing: The research usually begins with a hypothesis, a testable statement about the relationship between variables. Data is then used to either support or refute this hypothesis.
4. Statistical Analysis: The paper heavily relies on statistical methods to analyze the collected data. This could include descriptive statistics (mean, median, standard deviation) or inferential statistics (t-tests, regressions, etc.).
5. Formal Structure: A quantitative nursing research paper typically follows a structured format:
- Introduction: Provides background information, states the research question and hypothesis.
- Literature Review: Summarizes previous research relevant to the topic.
- Methodology: Describes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results: Presents the findings of the data analysis.
- Discussion: Interprets the results, discusses their significance, and connects them to existing literature.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the findings, highlights limitations, and suggests future research directions.
Examples of Quantitative Research Topics:
- The impact of social media use on mental health.
- The effectiveness of a new educational program.
- The relationship between income and life satisfaction.
- The prevalence of a particular disease in a specific population.
Key Differences from Qualitative Research:
While qualitative research focuses on understanding experiences, meanings, and perspectives through words and observations, quantitative research uses numbers and statistics to measure and analyze relationships between variables.
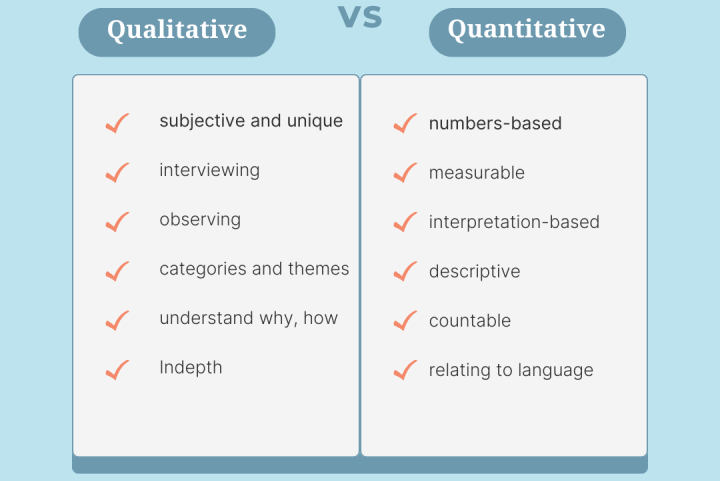
In summary: A quantitative research paper uses numerical data and statistical analysis to objectively explore and analyze a topic, aiming to test hypotheses and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence.
How to Write a Quantitative Nursing Research Paper
1. Laying the Foundation: Choosing a Relevant Topic and Framing the Research Question
The journey begins with identifying a research topic that is both relevant to current nursing practice and addresses a gap in existing knowledge. A well-defined research question forms the bedrock of your quantitative nursing research paper, guiding the entire research process.
Tips for Choosing a Relevant Topic:
- Seek inspiration from clinical practice: Observe your everyday interactions with patients and identify areas where research can improve outcomes, enhance understanding of patient needs, or refine existing interventions.
- Explore existing literature: Dive into published quantitative nursing research papers, reviews, and meta-analyses to identify emerging trends, unanswered questions, and areas ripe for further investigation.
- Attend conferences and workshops: Engage with experts in your field to gain insights into current research agendas and identify potential research topics.
- Collaborate with colleagues: Brainstorming with colleagues can spark innovative ideas and lead to collaborative research projects.
Formulating a Compelling Research Question:
- Specificity: Your research question should be clear, focused, and well-defined, avoiding vague or overly broad inquiries.
- Measurability: The question should lend itself to quantitative data collection and analysis, allowing for objective measurement of outcomes.
- Relevance: The question should align with current knowledge gaps and address a significant issue within nursing practice.
- Feasibility: Consider the resources, time, and expertise available to conduct the research and ensure the question is realistically achievable.
2. Building a Strong Framework: Choosing an Appropriate Design and Methodology
The design and methodology of your quantitative nursing research paper are crucial for ensuring the validity and reliability of your findings. Selecting the right approach will depend on the nature of your research question, the type of data you intend to collect, and the desired level of control over variables.
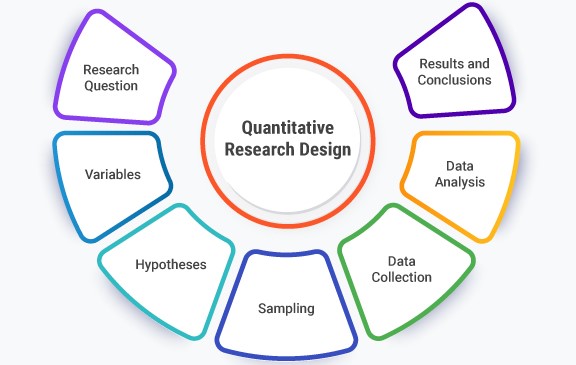
Common Quantitative Research Designs:
- Experimental designs: Randomly assigning participants to intervention and control groups to determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- Quasi-experimental designs: Investigating relationships between variables without random assignment, offering valuable insights but limiting causal inferences.
- Descriptive designs: Gathering information about a specific population or phenomenon, providing insights into prevalence, characteristics, and trends.
- Correlational designs: Examining the strength and direction of relationships between two or more variables, exploring potential associations.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Methods:
- Surveys: Gathering information from a large sample through structured questionnaires, useful for exploring attitudes, beliefs, and experiences.
- Interviews: Conducting structured or semi-structured conversations with participants to gain in-depth perspectives and detailed information.
- Observations: Systematically observing and recording behaviors or events, providing insights into real-world practices and interactions.
- Physiological measurements: Collecting objective data on physiological indicators, such as blood pressure, heart rate, or respiratory function, to assess physical health and well-being.
3. Crafting the Narrative: Writing a Compelling Introduction and Literature Review
A strong introduction sets the stage for your quantitative nursing research paper, captivating the reader and establishing the context for your research. The literature review provides a comprehensive overview of existing research, highlighting relevant theories, methodologies, and findings that underpin your investigation.
Writing an Engaging Introduction:
- Start with a compelling hook: Open with a captivating anecdote, a striking statistic, or a thought-provoking question to draw the reader in.
- Clearly state the research problem: Outline the issue or gap in knowledge that your research addresses, emphasizing its significance to nursing practice.
- Define key terms: Introduce essential concepts and terms, ensuring clarity and understanding for the reader.
- Provide a brief overview of the study: Outline the research question, the design, and the anticipated outcomes of your investigation.
Conducting a Comprehensive Literature Review:
- Identify relevant databases and sources: Explore databases such as PubMed, CINAHL, and Cochrane Library, along with professional journals and reputable websites.
- Establish clear search terms: Use a combination of keywords and Boolean operators to refine your search and retrieve relevant articles.
- Critically analyze sources: Evaluate the credibility, methodology, and findings of each article, identifying potential biases and limitations.
- Synthesize findings: Organize the literature into themes or categories, highlighting key findings, areas of agreement and disagreement, and emerging trends.
- Identify gaps in knowledge: Highlight unanswered questions and areas for further research, setting the stage for your study’s contribution.
4. Methodological Rigor: Providing a Detailed Account of the Research Process
The methodology section serves as the blueprint of your quantitative nursing research paper, outlining the research design, participants, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques.
Elements of a Robust Methodology Section:
- Research design: Describe the specific type of design you employed (experimental, quasi-experimental, descriptive, or correlational) and justify its suitability for your research question.
- Participants: Detail the characteristics of the participants, including their age, gender, health status, and any relevant demographic factors, specifying the sampling method used and the sample size.
- Data collection: Outline the instruments or tools used to collect data, including questionnaires, interview protocols, observation checklists, or physiological measurement devices.
- Data analysis: Describe the statistical techniques used to analyze the data, specifying the software used and the types of statistical tests employed.
- Ethical considerations: Address the ethical implications of the study, outlining informed consent procedures, data security measures, and any potential risks or benefits to participants.

5. Unveiling Insights: Presenting and Interpreting the Findings
The results section presents the quantitative data collected and analyzed in a clear and concise manner, using tables, figures, and statistical descriptions to illustrate key findings.
Tips for Presenting Results Effectively:
- Use appropriate tables and figures: Choose visual aids that effectively convey complex data, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding.
- Provide descriptive statistics: Summarize the data using measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and variability (standard deviation, range).
- Report inferential statistics: Present the results of statistical tests, including p-values and effect sizes, to demonstrate the significance of the findings.
- Present findings in a logical sequence: Organize the results according to the research questions or hypotheses, ensuring a coherent narrative flow.
Interpreting Findings Meaningfully:
- Relate findings to existing literature: Connect your findings to the theoretical framework and relevant studies reviewed in the literature review, highlighting areas of agreement and disagreement.
- Discuss the implications of the findings: Explain the practical significance of your results, suggesting potential implications for nursing practice, policy, or future research.
- Acknowledge limitations: Be transparent about any potential limitations of the study, such as sampling bias, small sample size, or methodological constraints, acknowledging their influence on the findings.
6. Crafting a Powerful Discussion: Synthesizing Insights and Drawing Conclusions
The discussion section provides a critical analysis of the findings, weaving together the results with the existing literature to generate a cohesive understanding of the study’s implications.
Key Elements of a Strong Discussion Section:
- Summarize key findings: Briefly restate the main results of the study, emphasizing the most significant findings.
- Interpret findings in light of existing literature: Connect the findings to relevant theories, concepts, and previous research, highlighting areas of support or contradiction.
- Discuss the implications of the findings: Explore the practical significance of the results, suggesting how they can inform nursing practice, policy, or future research.
- Acknowledge limitations and future directions: Reflect on the limitations of the study and identify potential areas for future research to address unanswered questions or extend the scope of investigation.
7. Final Touches: Polishing and Submitting Your Manuscript
Once you have crafted a compelling narrative, it’s time to polish your manuscript to ensure clarity, accuracy, and adherence to publication guidelines.
Tips for Polishing Your Quantitative Nursing Research Paper:
- Revise and edit thoroughly: Check for clarity, conciseness, grammatical errors, and consistency in language and style.
- Seek feedback from colleagues: Request feedback from peers or mentors, ensuring clarity and objectivity in your writing.
- Follow journal guidelines: Adhere to the specific formatting and citation style of the target journal, paying attention to word limits and manuscript organization.
- Prepare a cover letter: Submit a concise cover letter that summarizes the study’s significance, highlighting its contributions to the field.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Quantitative Nursing Research Paper
Writing a strong quantitative nursing research paper requires meticulous attention to detail and adherence to specific methodological principles. Avoiding common pitfalls ensures a clear, accurate, and impactful presentation of your findings. Here are some mistakes to be wary of:
1. Inadequate Sample Size and Selection: A well-designed quantitative nursing research paper relies on a sample size large enough to represent the target population accurately. Failing to achieve this can lead to biased results and limit the generalizability of your findings.
2. Lack of Randomization and Control: A quantitative nursing research paper often benefits from randomization, ensuring participant groups are comparable. The absence of appropriate control measures can confound results and make it difficult to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
3. Inconsistent Data Collection and Analysis: Maintaining consistent methods across all data collection points is crucial in a quantitative nursing research paper. Inconsistent data analysis can introduce error and undermine the validity of your results.
4. Overlooking Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations are paramount in any quantitative nursing research paper. Failure to address issues like informed consent, confidentiality, and data security can compromise the integrity of your study and potentially harm participants.
5. Insufficient Data Presentation and Interpretation: A strong quantitative nursing research paper presents data clearly and interprets findings within the broader context of existing literature. Avoid relying solely on tables and graphs; provide clear explanations and discussions to illuminate the significance of your findings.
6. Ignoring Limitations and Future Directions: A quantitative nursing research paper should acknowledge its limitations, such as sample size, setting, or specific methods employed. This honesty strengthens the credibility of your work and helps guide future research efforts.
By diligently addressing these common pitfalls, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their quantitative nursing research papers, contributing valuable knowledge to the nursing profession and ultimately improving patient care.
The Journey of a Quantitative Nursing Research Paper
Writing an outstanding quantitative nursing research paper is an iterative process that requires dedication, perseverance, and a commitment to rigorous methodology and clear communication. Embrace the challenges, seek guidance from mentors, and strive for excellence in every stage of the research process.

By meticulously crafting your manuscript and adhering to these strategies, you can contribute to the advancement of nursing knowledge and improve patient outcomes. Remember, every quantitative nursing research paper is a valuable contribution to the body of nursing literature, shaping the future of the profession and empowering nurses to provide the best possible care.
Get Customized Nursing Research Paper Writing Assistance
At Nursing Papers, we understand the toll that assignment writing can have on students. Thus, we provide customized academic paper writing help for nursing research papers, essays, case studies and dissertations. We can assist you with choosing compelling topics, writing academic papers, proof reading and editing, and plagiarism removal.