Table of Contents
Nursing care plans are the cornerstone of safe and effective patient care. They serve as a roadmap for nurses, guiding them in providing individualized, holistic care that addresses the unique needs of each patient. However, crafting exceptional nursing care plans requires more than just ticking boxes; it demands a deep understanding of nursing principles, critical thinking skills, and a commitment to patient-centered care.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to writing stellar nursing care plans, ensuring that you’re not just meeting minimum standards, but exceeding them.
Understanding the Purpose of Nursing Care Plans
Before diving into the specifics of writing, it’s crucial to understand the core purpose of nursing care plans. They are not merely bureaucratic documents; they are dynamic tools used to:
- Individualize patient care: Nursing care plans allow nurses to tailor interventions to a specific patient’s condition, preferences, and goals. Generic plans are ineffective; each plan should reflect the unique circumstances of the individual.
- Promote continuity of care: They facilitate consistent care delivery across shifts and healthcare settings, ensuring that all healthcare providers are on the same page. This is especially important in busy hospital environments where multiple nurses may care for a single patient.
- Improve patient outcomes: By clearly outlining goals and interventions, nursing care plans enhance the likelihood of achieving desired patient outcomes, such as improved mobility, reduced pain, or better wound healing.
- Enhance communication: Nursing care plans serve as a powerful communication tool, facilitating clear and concise communication among healthcare team members, including physicians, physical therapists, and other specialists.
- Facilitate evaluation and revision: The plan provides a framework for ongoing assessment and evaluation, allowing for adjustments and modifications as the patient’s condition changes. Effective nursing care plans are constantly evaluated and revised.
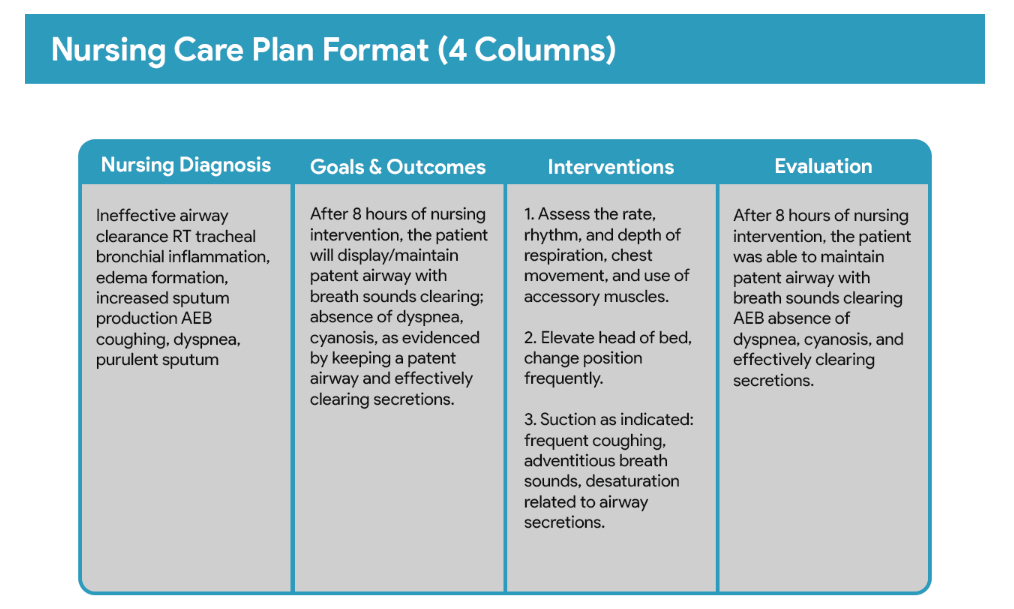
The Components of a Stellar Nursing Care Plan
A stellar nursing care plan is more than just a checklist; it’s a comprehensive and well-structured document. Key components include:
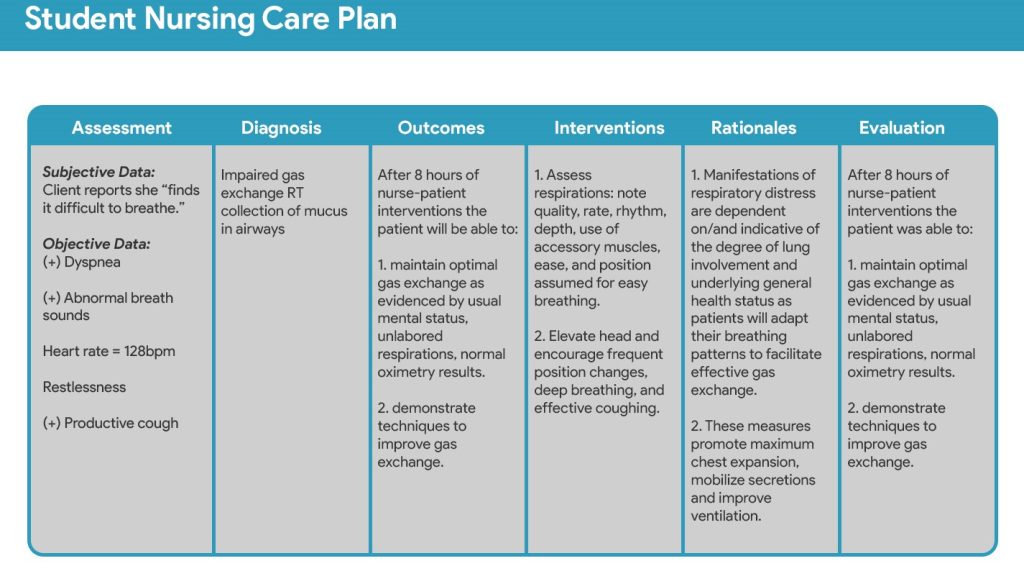
- Assessment: This is the foundation of any effective nursing care plan. It involves a thorough collection of subjective and objective data about the patient, including their medical history, current condition, vital signs, physical assessment findings, and psychosocial factors. This data forms the basis for identifying nursing diagnoses.
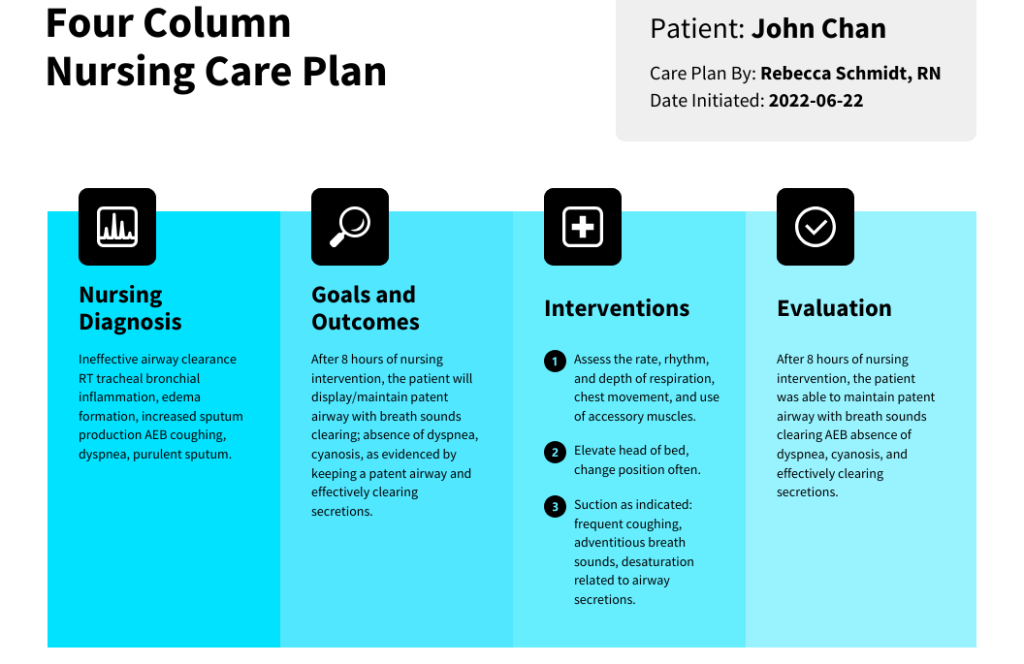
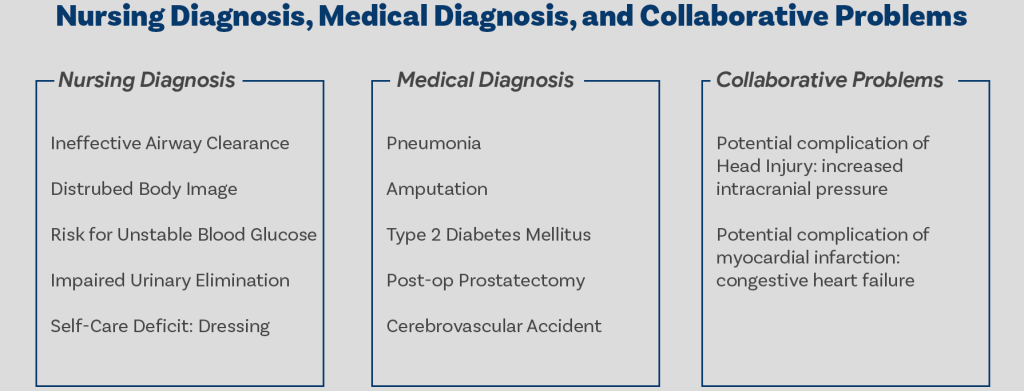
- Nursing Diagnoses: This section involves analyzing the assessment data to identify actual or potential health problems that the nurse can address. Nursing diagnoses use the NANDA-I (North American Nursing Diagnosis Association International) standardized language, ensuring clear and consistent communication. They should be specific, concise, and relevant to the patient’s situation. For example, instead of “pain,” a more precise diagnosis might be “acute pain related to surgical incision as evidenced by patient report of 8/10 pain and guarding behavior.”
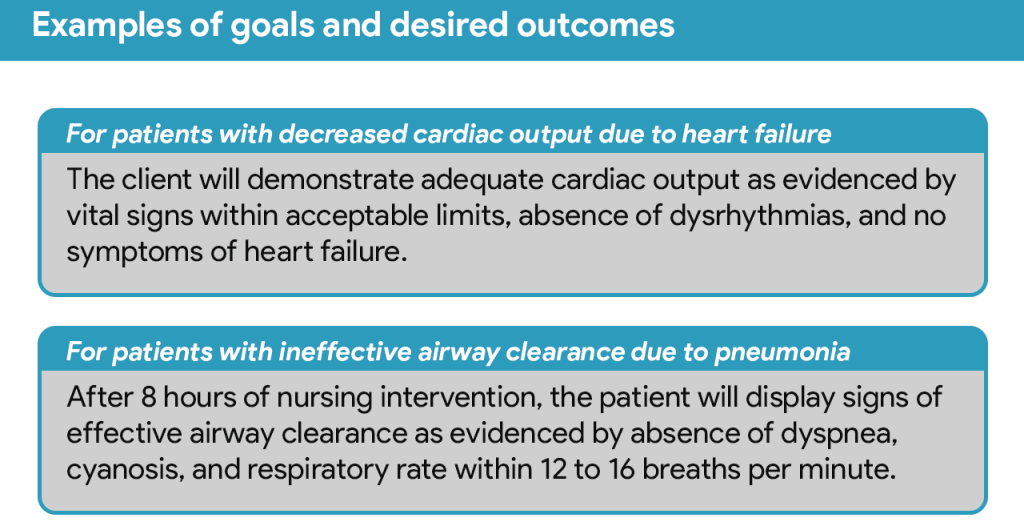
- Planning: This crucial step involves establishing realistic and measurable goals for the patient. These goals should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For example, “Patient will ambulate 50 feet with assistance by the end of the day” is a SMART goal. The planning phase also involves identifying nursing interventions – the specific actions the nurse will take to achieve the established goals. These interventions should be evidence-based and tailored to the individual patient.
- Implementation: This is the action phase where the nurse carries out the planned interventions. Detailed documentation of the implemented interventions is crucial, including the time, method, and patient response. This meticulous documentation is essential for tracking progress and making adjustments as needed.
- Evaluation: This is the final and arguably most important stage. The evaluation section involves assessing the effectiveness of the implemented interventions in achieving the established goals. Was the patient able to ambulate as planned? Did their pain level decrease? The evaluation should be objective and supported by data. If the goals were not met, the nursing care plan must be revised, adjusting the interventions or goals as necessary.
Essential Tips for Writing Stellar Nursing Care Plans
- Prioritize patient-centered care: Always put the patient’s needs and preferences at the forefront. Involve the patient and their family in the planning process whenever possible.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid medical jargon and use language that is easily understood by all members of the healthcare team.
- Be specific and detailed: Avoid vague statements. Clearly describe the interventions and desired outcomes.
- Use evidence-based practice: Base your interventions on current research and best practices.
- Maintain accurate and up-to-date documentation: Regularly review and update the nursing care plan as the patient’s condition changes.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team: Work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians and physical therapists, to ensure comprehensive care.
- Utilize available resources: Consult resources such as nursing textbooks, journals, and online databases to enhance your knowledge and improve your care planning skills.
- Regularly review and revise your nursing care plans: Even the best-laid nursing care plans require ongoing evaluation and revision. Regularly reassess the patient’s condition and adjust the plan as needed. This iterative process ensures that the nursing care plan remains relevant and effective.
- Seek feedback from colleagues: Don’t hesitate to ask for feedback from experienced nurses. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your nursing care plan writing skills.
Avoiding the Common Pitfalls in Writing Nursing Care Plans
Nursing care plans are the cornerstone of safe and effective patient care. They provide a roadmap for nurses, outlining individualized interventions to address patient needs and achieve desired outcomes. However, even experienced nurses can fall prey to common pitfalls that compromise the quality and usefulness of these vital documents. Understanding these pitfalls and implementing preventative strategies is crucial for optimizing patient care and improving overall nursing practice.
1. Lack of Specificity and Measurable Goals: A common mistake is setting vague goals like “improve patient mobility” or “manage pain.” These are insufficient for guiding interventions and evaluating progress. An effective nursing care plan requires specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
How to avoid it: Instead of “improve patient mobility,” write “Patient will ambulate 50 feet with assistance by end of shift.” Quantifiable data allows for objective assessment of progress. Clearly define what constitutes “improved” or “managed” in relation to each patient’s unique baseline.
2. Inadequate Assessment Data: A nursing care plan must be grounded in thorough and accurate patient assessments. Without comprehensive data, interventions might be inappropriate or ineffective. Insufficient data also makes it difficult to demonstrate the rationale behind the chosen nursing diagnoses.
How to avoid it: Conduct a comprehensive assessment, including physical examination, patient history, and review of relevant medical records. Document findings meticulously, using precise language and avoiding subjective interpretations. Consider using standardized assessment tools to ensure consistency and completeness. Remember to re-assess the patient regularly and adjust the nursing care plans accordingly.
3. Ignoring Patient Preferences and Values: Effective nursing care plans consider the patient’s individual needs, preferences, and values. Failing to do so can lead to interventions that are ineffective or even counterproductive, potentially compromising patient satisfaction and adherence to the treatment plan.
How to avoid it: Engage patients actively in the care planning process. Involve them in setting goals, discussing options, and making informed decisions about their care. Document their preferences and values clearly within the nursing care plan, ensuring that interventions align with their wishes.
4. Overlooking Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Communication: A nursing care plan is not an isolated document. Effective plans require communication and collaboration with other healthcare professionals, including physicians, physical therapists, and social workers. Failure to coordinate care can result in conflicting interventions and fragmented care.
How to avoid it: Facilitate interdisciplinary communication by actively participating in care conferences and documenting all relevant interactions. Clearly communicate the nursing care plan’s goals and interventions to other members of the healthcare team. Ensure the plan reflects the collaborative contributions of all relevant professionals.
5. Inconsistent Documentation and Lack of Revision: Nursing care plans are dynamic documents that should be regularly reviewed and revised as the patient’s condition changes. Inconsistent documentation or a failure to update the plan as needed can lead to inaccurate records and potentially compromise patient safety.
How to avoid it: Document all nursing interventions, patient responses, and changes in condition promptly and accurately. Regularly review every nursing care plan with the patient and the healthcare team. Update the plan as needed, reflecting the evolving needs of the patient. Ensure that the nursing care plan is legible, concise, and easily understandable by all members of the healthcare team.
6. Failing to Prioritize Interventions: A nursing care plan often includes a long list of interventions. Prioritizing these interventions based on urgency and importance is essential to avoid overwhelming the patient and healthcare providers.
How to avoid it: Use prioritization frameworks, such as Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs or ABC (airway, breathing, circulation) priorities. Focus on the most critical needs first, and then address less urgent interventions as resources allow. Clearly indicate the priority of each intervention within the nursing care plan.
By diligently addressing these potential pitfalls, nurses can create comprehensive, accurate, and effective nursing care plans that promote the best possible patient outcomes. The time investment in developing a robust nursing care plan is crucial, as it leads to improved patient safety, enhanced communication among the healthcare team, and a higher quality of care overall.
Technology and Nursing Care Plans
Technology is rapidly changing the way nursing care plans are developed and managed. Electronic health records (EHRs) and specialized software programs are increasingly used to create, document, and track nursing care plans. These systems offer several advantages, including improved efficiency, enhanced communication, and better data management. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the technology used complements, rather than hinders, the core principles of patient-centered care and effective communication. The technology should facilitate, not replace, the human element of nursing care.

Frequently Asked Questions about Nursing Care Plans
Nursing care plans are the cornerstone of safe and effective patient care. They serve as a roadmap, guiding nurses in providing individualized, holistic treatment. However, the very concept of nursing care plans can seem daunting, especially to those new to the field. This section addresses the most frequently asked questions surrounding these crucial documents, demystifying their purpose and application.
What is a Nursing Care Plan?
This is perhaps the most fundamental question. Simply put, nursing care plans are detailed, individualized documents that outline the care a patient will receive. They’re not generic templates; instead, they’re tailored to each patient’s unique needs, medical history, and current condition. These plans encompass assessments, diagnoses (nursing diagnoses, not medical diagnoses), goals, interventions, and evaluation methods.
They’re essentially a blueprint for providing the best possible nursing care, ensuring consistent and high-quality treatment. The creation and implementation of effective nursing care plans require a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s overall health status and anticipated needs.
Why are Nursing Care Plans Important?
The importance of nursing care plans is multifaceted. First, they ensure continuity of care. Multiple nurses may care for a single patient during a shift or over a period of days. The nursing care plan acts as a common reference point, guaranteeing that all healthcare providers are on the same page and delivering consistent, coordinated care. This reduces the risk of errors and inconsistencies in treatment.
Secondly, they promote individualized care. By focusing on specific patient needs, nursing care plans allow nurses to tailor their interventions accordingly. This personalized approach significantly enhances patient outcomes and satisfaction. Furthermore, they facilitate effective communication between healthcare professionals. The plan acts as a central repository of information, readily accessible to all members of the care team. This transparent approach promotes better teamwork and improves the overall quality of care. Finally, a nursing care plan serves as legal documentation, protecting both the patient and the healthcare provider. They provide a detailed record of the care provided, which is crucial for accountability and legal purposes.
How are Nursing Care Plans Developed?
Developing a comprehensive nursing care plan is a systematic process. It begins with a thorough assessment of the patient, including their medical history, current condition, physical and mental status, and psychosocial factors. This assessment informs the identification of nursing diagnoses, which describe the patient’s actual or potential health problems. Based on these diagnoses, measurable goals are established, outlining the desired outcomes of care.
Next, interventions are planned, outlining the specific nursing actions that will be taken to achieve those goals. Finally, evaluation methods are established to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the plan as the patient’s condition changes. This cyclical process ensures that the nursing care plan remains relevant and effective throughout the patient’s treatment.
What are the common components of a Nursing Care Plan?
A typical nursing care plan includes several key components: the patient’s assessment data (vital signs, medical history, etc.), nursing diagnoses (e.g., impaired mobility, risk for infection), planned goals (e.g., patient will ambulate with assistance by day 3), nursing interventions (e.g., assist patient with ambulation twice daily, monitor for signs of infection), evaluation of interventions (e.g., patient ambulated with minimal assistance on day 3, no signs of infection noted), and any relevant documentation regarding the patient’s response to treatment and progress towards goals. These components work in tandem to provide a holistic view of the patient’s care journey.
What if the Patient’s Condition Changes?
A nursing care plan isdynamic and should be updated regularly to reflect changes in the patient’s condition. Any significant alterations – such as a change in medical status, response to treatment, or the emergence of new problems – necessitate revisions to the plan. This ensures that the care provided remains appropriate and effective. Regular evaluation and adjustment are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.
A nursing care plan is an essential tool for providing safe, effective, and individualized patient care. Understanding their purpose, components, and development process is crucial for all healthcare professionals involved in patient care. While the process may seem complex initially, the benefits far outweigh the effort, leading to improved patient outcomes and a more efficient, organized approach to nursing practice. Care plans are not just bureaucratic necessities; they are vital instruments in the pursuit of high-quality patient care.
Conclusion:
Developing stellar nursing care plans is a crucial skill for any nurse. These plans are not just documents to be filed away; they are dynamic tools that guide safe, effective, and patient-centered care. By adhering to the principles and guidelines outlined in this article, nurses can create nursing care plans that significantly improve patient outcomes and contribute to a high-quality healthcare experience.

The goal is not just to complete the nursing care plans, but to use them as a roadmap to provide exceptional care, ensuring that each patient receives the individualized attention they deserve. The consistent implementation and thoughtful revision of nursing care plans are paramount to ensuring optimal patient care. Proficiently crafted nursing care plans ultimately translate to better patient health, improved satisfaction, and a more efficient healthcare system. Mastering the art of writing nursing care plans is an ongoing process, and continued learning and refinement are key to achieving excellence in this essential aspect of nursing practice.
Get Professional Nursing Care Plan Writing Service
Are you struggling with writing nursing care plans? Then, let the experts at Nursing Papers help you. We offer professional help with writing care plans for nursing students. Besides writing the care plan, we will also do proofreading, editing and formatting to ensure a flawless paper. Our writers can also assist you with writing essays, research papers, case studies and dissertations.