Table of Contents
The nursing literature review is a cornerstone of academic and professional development. It’s a crucial step in building a strong foundation for research, practice, and policy. However, navigating the vast and ever-expanding world of nursing literature can feel like traversing a complex labyrinth.
The following guide offers effective strategies to help you craft a compelling and impactful literature review for your nursing paper. It also offers suggestions on the best places to find high quality nursing research paper samples to inspire you on this endeavor.
What is a Nursing Literature Review?
A nursing literature review is a systematic and critical analysis of existing research on a specific topic within the field of nursing. It’s a comprehensive and objective examination of published studies, articles, and other relevant literature to synthesize current knowledge, identify gaps in research, and provide a foundation for further investigation or practice improvement.
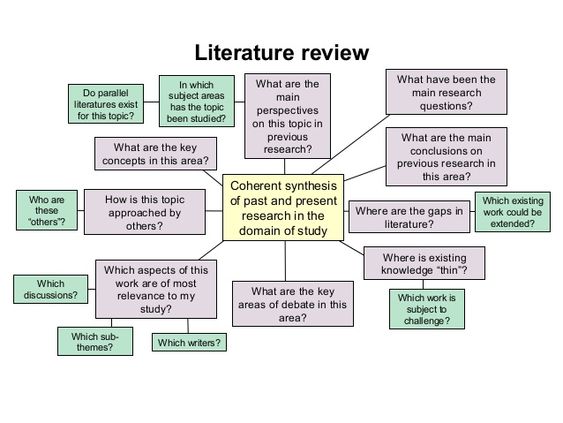
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of a literature review for a nursing paper:
Purpose:
- Synthesize Existing Knowledge: To gather and present a concise summary of what is known about a particular nursing topic.
- Identify Gaps in Research: To highlight areas where further investigation is needed, pointing out limitations in current studies or unanswered questions.
- Inform Nursing Practice: To provide evidence-based information that can guide nursing practice, policy development, and decision-making.
- Support Research Proposals: To provide a foundation for new research studies, justifying the need for further investigation.
Characteristics:
- Systematic and Comprehensive: It involves a structured approach to searching, selecting, and evaluating relevant literature using specific criteria.
- Critical Analysis: It goes beyond simply summarizing findings; it critically evaluates the quality, validity, and relevance of the research.
- Objective and Balanced: It presents a neutral and balanced perspective on the literature, avoiding personal opinions or biases.
- Organized and Clear: It has a logical structure and uses clear language to present the synthesized information in a concise and engaging way.
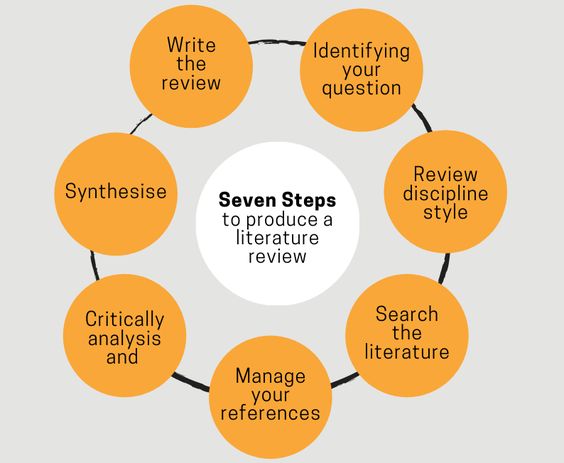
Steps Involved:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the research question, PICO elements, and time frame for the review.
- Search for Literature: Utilize multiple databases and keywords to identify relevant articles and publications.
- Critically Appraise the Literature: Evaluate the quality, methodology, and potential biases of the selected studies.
- Synthesize the Findings: Group and analyze the findings, identifying commonalities, discrepancies, and key conclusions.
- Structure and Organize: Choose an appropriate organizational framework (chronological, thematic, methodological) to present the synthesized information.
- Write and Edit: Craft a clear, concise, and engaging narrative, using objective language and appropriate referencing.
- Seek Feedback and Revise: Obtain feedback from peers or mentors to improve clarity, organization, and overall effectiveness.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Understanding: Provides a deeper understanding of a specific nursing topic and its current state of research.
- Evidence-Based Practice: Provides a foundation for making informed decisions based on the best available evidence.
- Identifies Gaps and Opportunities: Highlights areas where further research is needed or where practice improvements can be implemented.
- Advances Nursing Knowledge: Contributes to the ongoing development and refinement of nursing knowledge and practice.
In essence, the literature review acts as a bridge between existing research and its application in clinical practice, research, and policy. It provides a crucial foundation for making informed decisions and advancing the field of nursing.
1. Setting the Stage for Your Nursing Literature Review
The first step is to clearly define the scope of your literature review. This includes:
- Identifying your research question: A well-defined question provides a clear focus for your review. It guides your search for relevant literature and ensures your review remains focused.
- Specifying the population, intervention, comparison, and outcome (PICO) elements: This framework helps you narrow down your search and pinpoint the specific area of interest within your chosen topic.
- Defining the time frame: This ensures that you include the most current and relevant research, while also considering the historical context of your topic.
Example:
“This nursing literature review aims to investigate the effectiveness of patient education programs on adherence to medication regimens for patients with type 2 diabetes in the past five years.”
Defining the scope sets the stage for a structured and relevant literature review.
2. Unearthing the Right Literature for The Review
Once your scope is defined, you need to locate the relevant literature. Here’s how to search for the right literature for your review.
- Utilize multiple databases: Don’t limit yourself to just one database. Explore options like PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar and Scopus to ensure comprehensive coverage. You can also check out nursing paper samples from educational websites such as phdnursewriter.com for inspiration.
- Employ appropriate keywords: Use relevant keywords based on your PICO elements, along with synonyms and variations.
- Refine your search: Employ Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to refine your search and exclude irrelevant articles.
- Utilize filters: Take advantage of filters for publication date, study design, and language to narrow down your search results.
3. Critical Appraisal: Sifting through the Information
The next step involves critically evaluating the resources you have found. Doing so helps determine the quality and relevance of the sources for your literature review:
- Assess the credibility of the source: Pay attention to the author’s credentials, the publication’s reputation, and the study’s funding source.
- Evaluate the study design: Different research designs have different strengths and weaknesses. Consider the study’s methodological rigor, sample size, and statistical analysis.
- Look for bias: Be aware of potential biases in the study design, data analysis, and interpretation of findings.
- Identify the limitations: Recognize and acknowledge any limitations in the study’s design or findings.
4. Synthesizing the Findings: Weaving a Narrative for Your Review
After critically appraising the selected literature, you must synthesize the findings to present a clear and concise narrative:
- Group related articles: Categorize the articles based on their key themes, findings, or methodological approaches.
- Identify commonalities and discrepancies: Highlight the shared findings and any contradictory or conflicting evidence.
- Draw conclusions: Summarize the key findings and their implications for nursing practice, research, and policy.
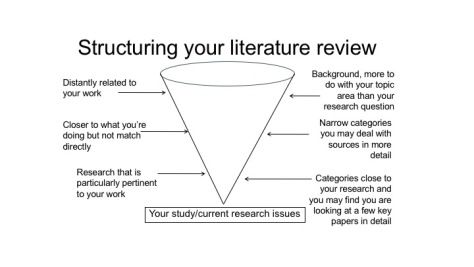
5. Structure and Organization: Crafting a Coherent Narrative
A well-structured nursing literature review enhances clarity and readability. Consider the following organizational frameworks:
- Chronological: Present the literature in chronological order, tracing the evolution of the topic and identifying shifts in understanding.
- Thematic: Organize the review around specific themes or concepts, highlighting the different perspectives and arguments within the literature.
- Methodological: Group articles based on their research design, such as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods.

6. Writing Style: How to Engage the Reader
Writing a literature review goes beyond simply summarizing articles. Instead, it involves crafting a compelling and engaging narrative:
- Use a clear and concise writing style: Avoid jargon and technical terms. Use clear and simple language to ensure accessibility for a broad audience.
- Provide sufficient context: Introduce the topic and its relevance to nursing practice.
- Be objective: Present the findings of the literature objectively, avoiding personal opinions or biases.
- Use transitions effectively: Employ transition words and phrases to connect ideas and ensure a smooth flow between sections.
- Maintain a consistent voice and tone: Use a consistent voice and tone throughout the review, ensuring the language is professional and appropriate for the intended audience.
7. Adding Depth and Critical Analysis
You should incorporate critical analysis and insightful observations to elevate the literature review beyond a simple summary.
- Identify gaps in the literature: Highlight areas where research is lacking or where more investigation is needed.
- Discuss the implications of the findings: Explore the implications of the literature for nursing practice, policy, and future research.
- Offer recommendations: Suggest areas for future research, interventions, or policy changes based on the findings.
- Consider alternative perspectives: Explore alternative perspectives on the topic and acknowledge the limitations of current research.
8. Referencing and Formatting: Ensuring Accuracy and Consistency
Accurate referencing and proper formatting are crucial for maintaining credibility and consistency in every nursing literature review:
- Follow a specific referencing style: Choose a referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) and consistently apply it throughout the review.
- Use a consistent format for citations: Ensure all citations are formatted accurately and consistently.
- Provide a complete reference list: Include all sources cited in the review in a separate reference list at the end of the document.
9. Examples of Effective Nursing Literature Reviews
To gain inspiration and insights, explore well-written literature reviews in your area of interest. Search for published articles in reputable nursing journals or consult online databases for examples. Pay attention to their structure, writing style, and critical analysis.
10. Feedback and Revision: Polishing The Literature Review
Before submitting your nursing literature review, seek feedback from trusted peers or mentors. They can provide valuable insights on the clarity, organization, and overall effectiveness of your work. Incorporate their feedback to revise and refine your review.Crafting a strong is literature review requires meticulous planning, thorough research, and a critical eye.

The strategies discussed above can help you to navigate the labyrinth of nursing literature, unearth relevant findings, and present a compelling and impactful review that contributes to the advancement of nursing knowledge, practice, and policy. A well-crafted nursing literature review serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, evidence-based practice, and the pursuit of new knowledge. It’s not just a summary of existing research; it’s a recipe for shaping the future of nursing.
Hire Professional Nursing Literature Review Writing Service
Writing a literature review is not just an assignment; it’s a journey of discovery. As such, crafting a compelling piece requires outstanding writing skills, commitment and time. That is why you need a professional nursing literature review writing service to get through the labyrinth. At nursingpapers.us, we guarantee the best writing services for all types of nursing essays, case studies, research papers and dissertations. Get in touch with us for professional help with crafting compelling literature reviews.