Table of Contents
Nursing, as a profession, stands at the vanguard of healthcare delivery, constantly evolving to meet the dynamic needs of patients, communities, and the healthcare system itself. At the heart of this evolution lies robust nursing research. Engaging in research allows nurses to contribute to evidence-based practice, improve patient outcomes, shape health policy, and advance the profession. However, identifying impactful and relevant research topics for nursing can be a daunting task for students and seasoned professionals alike.
The sheer breadth of the field, coupled with the rapid advancements in medical science and technology, presents a vast landscape of potential inquiry. This article aims to illuminate this landscape by exploring ten prominent research topics for nursing that are currently shaping the future of healthcare, offering a springboard for innovation and discovery. Selecting the right research topics for nursing is crucial for a successful and meaningful investigation.
The importance of continuously generating new knowledge through research cannot be overstated. As healthcare challenges become more complex, from managing chronic diseases in an aging population to addressing global health crises, the need for insightful and practical research topics for nursing grows. These investigations provide the foundation for interventions that enhance patient safety, optimize care delivery, and promote health equity. This exploration will delve into areas ripe for investigation, providing a solid foundation for those seeking to contribute to the ever-expanding body of nursing knowledge. These research topics for nursing are selected for their contemporary relevance and potential impact.
The Significance of Choosing Relevant Research Topics for Nursing
Before diving into specific areas, it’s essential to understand why the selection process for research topics for nursing is so critical. A well-chosen topic:
- Addresses a genuine gap in knowledge: It seeks to answer questions that haven’t been adequately explored.
- Has practical implications: The findings can be translated into improved nursing practice or patient care.
- Is feasible to investigate: The researcher has access to the necessary resources, population, and expertise.
- Aligns with the researcher’s passion and interest: This fuels motivation and perseverance throughout the research process.
- Contributes to the broader healthcare dialogue: Good nursing research topics often have interdisciplinary relevance.

With these considerations in mind, let’s explore ten compelling research topics for nursing.
Top 10 Nursing Research Topics for 2025 and Beyond
1. Mental Health in Diverse Patient Populations
Mental health is increasingly recognized as an integral component of overall well-being. However, disparities in access to and quality of mental healthcare persist, particularly among diverse and underserved populations. This makes mental health one of the most pressing research topics for nursing. Nurses are often the first point of contact for individuals experiencing mental health challenges, making their role crucial.
Potential Research Areas:
- Culturally Sensitive Mental Health Interventions: Developing and evaluating nursing interventions that are tailored to the specific cultural beliefs, values, and practices of diverse ethnic groups. This is a vital subset of research topics for nursing.
- Impact of Social Determinants on Mental Health: Investigating how factors like poverty, discrimination, housing instability, and education level affect mental health outcomes in specific communities and the role nurses can play in mitigation.
- Mental Health Stigma Reduction: Exploring nurse-led strategies to reduce stigma associated with mental illness within healthcare settings and communities.
- Integration of Mental and Physical Healthcare: Examining effective models for integrating mental health screening and care into primary care settings, led or supported by nurses. This remains a significant focus for research topics for nursing.
- Tele-Mental Health Nursing: Assessing the efficacy, accessibility, and patient satisfaction with tele-mental health services provided by nurses, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Exploring these research topics for nursing can lead to significant improvements in mental healthcare access and quality for all.
2. The Impact of Technology on Nursing Care and Patient Outcomes
Technology is revolutionizing healthcare, from electronic health records (EHRs) and telehealth to artificial intelligence (AI) and wearable devices. Understanding how technology impacts nursing workflow, patient safety, and outcomes is a critical area for investigation and constitutes many emerging research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- EHR Usability and Nurse Burnout: Examining the relationship between EHR design, usability, documentation burden, and the prevalence of burnout among nurses.
- Telehealth Effectiveness in Chronic Disease Management: Evaluating the impact of nurse-led telehealth interventions on self-management, adherence, and clinical outcomes for patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. This is a timely example of research topics for nursing.
- AI in Clinical Decision Support for Nurses: Investigating the accuracy, utility, and ethical implications of AI-powered tools designed to assist nurses in clinical decision-making.
- Wearable Technology and Patient Monitoring: Assessing the role of wearable devices in remote patient monitoring by nurses and their impact on early detection of health deterioration.
- Cybersecurity and Patient Data Privacy: Exploring nurses’ awareness, preparedness, and role in maintaining cybersecurity and protecting patient data in an increasingly digital healthcare environment. Many research topics for nursing now intersect with data security.
These nursing research topics are crucial for ensuring technology enhances, rather than hinders, quality nursing care.
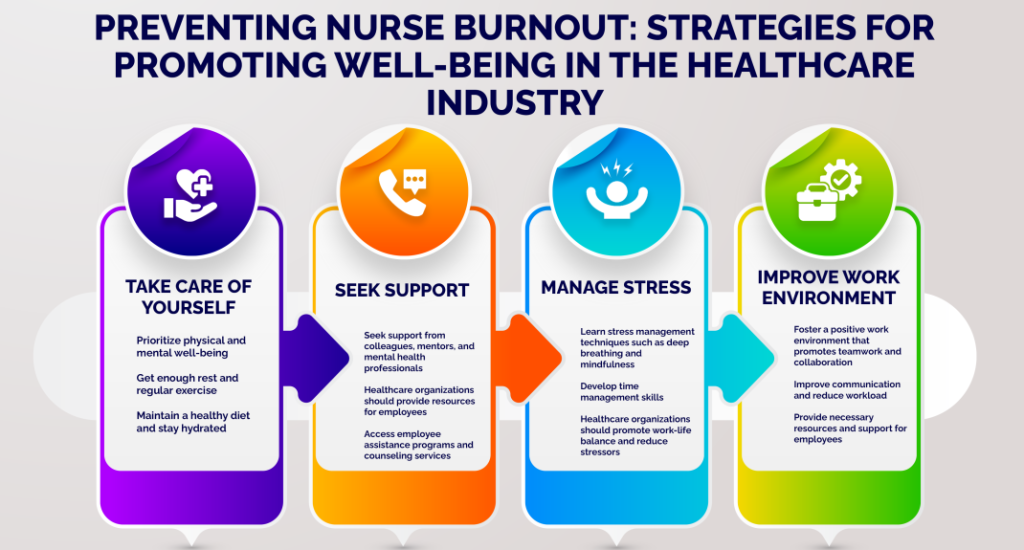
3. Addressing Nurse Burnout and Promoting Well-being
The nursing profession is inherently demanding, and issues like understaffing, long hours, and high emotional labor contribute significantly to nurse burnout, compassion fatigue, and turnover. Investigating strategies to support nurses’ well-being is paramount, making this one of the most important research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Effectiveness of Resilience-Building Programs: Evaluating the impact of mindfulness-based stress reduction, resilience training, and other interventions on nurses’ stress levels, coping mechanisms, and job satisfaction.
- Organizational Factors Contributing to Burnout: Identifying specific workplace characteristics (e.g., leadership styles, staffing ratios, workplace culture) that exacerbate or mitigate nurse burnout.
- Impact of Peer Support Programs: Assessing the effectiveness of formal and informal peer support systems in reducing stress and improving well-being among nurses.
- Work Schedule Innovations: Exploring the effects of alternative work schedules, flexible staffing models, and mandatory break policies on nurse fatigue and patient safety. This is a practical avenue for research topics for nursing.
- Moral Distress and Ethical Dilemmas: Investigating the prevalence and impact of moral distress among nurses and developing interventions to support ethical decision-making and coping. Such research topics for nursing directly address the lived experiences of nurses.
4. Enhancing Patient Safety and Quality Improvement
Patient safety remains a cornerstone of high-quality healthcare. Nurses play a pivotal role in preventing medical errors, managing risks, and implementing quality improvement initiatives. This domain offers a wealth of research topics for nursing focused on creating safer care environments.
Potential Research Areas:
- Medication Error Reduction Strategies: Developing and testing innovative nurse-led interventions to reduce medication administration errors (e.g., use of technology, improved communication protocols).
- Fall Prevention in Vulnerable Populations: Evaluating the effectiveness of multifactorial fall prevention programs implemented by nurses in hospitals, long-term care facilities, or home care settings.
- Improving Handoff Communication: Investigating standardized communication tools and processes (e.g., SBAR) to enhance the safety and effectiveness of patient handoffs between nurses and across shifts. This is a classic yet still relevant area for research topics for nursing.
- Patient Engagement in Safety Initiatives: Exploring strategies to effectively involve patients and their families in identifying and mitigating safety risks.
- Impact of Nursing Staffing Levels on Patient Outcomes: Further research into the correlation between nurse-to-patient ratios, skill mix, and specific patient safety indicators (e.g., hospital-acquired infections, pressure ulcers). Many research topics for nursing revolve around this critical issue.
5. Geriatric Nursing and Care for the Aging Population
The global population is aging rapidly, presenting unique healthcare challenges and increasing the demand for specialized geriatric care. Nurses are at the forefront of caring for older adults across various settings. This demographic shift makes geriatric care a key area for research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Management of Polypharmacy in Older Adults: Developing and evaluating nurse-led interventions to optimize medication regimens and reduce adverse drug events in elderly patients.
- Dementia Care Strategies: Investigating innovative, person-centered care models for individuals with dementia, focusing on behavioral management, communication techniques, and caregiver support.
- Promoting Functional Independence in Older Adults: Evaluating the effectiveness of nursing interventions aimed at maintaining or improving physical and cognitive function in the elderly.
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care for Geriatric Patients: Exploring best practices for providing compassionate and effective palliative care and addressing the unique end-of-life needs of older adults and their families. This is a deeply important category of research topics for nursing.
- Elder Abuse Detection and Prevention: Developing and validating screening tools and intervention strategies for nurses to identify and prevent elder abuse and neglect.
6. Chronic Disease Management and Self-Management Support
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory conditions, and cancer are leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Nurses play a critical role in managing these conditions and empowering patients to self-manage their health. Consequently, this area offers many pertinent research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Effectiveness of Nurse-Led Self-Management Education Programs: Evaluating the impact of tailored education and coaching on patient knowledge, self-efficacy, adherence, and clinical outcomes for specific chronic diseases.
- Health Literacy and Chronic Disease Outcomes: Investigating the relationship between health literacy levels and patients’ ability to manage their chronic conditions, and developing nurse-led interventions to address low health literacy.
- Role of Family and Social Support in Chronic Care: Exploring how nurses can engage family members and leverage social support systems to improve outcomes for patients with chronic illnesses.
- Transition of Care for Patients with Chronic Conditions: Examining nurse-led strategies to improve care coordination and reduce hospital readmissions for patients transitioning from hospital to home or other care settings. This is a significant system-level nursing research topic suggestion.
- Behavioral Change Interventions: Investigating the effectiveness of motivational interviewing and other behavioral change techniques employed by nurses to promote healthy lifestyle choices (e.g., diet, exercise, smoking cessation) in patients with chronic diseases. These research topics for nursing have direct behavioral impact.
7. Health Equity and Addressing Disparities
Health disparities, defined as differences in health outcomes linked to social, economic, or environmental disadvantage, persist across various populations. Nurses are uniquely positioned to advocate for health equity and implement interventions that address these disparities. This makes health equity a profoundly important domain for research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Impact of Implicit Bias in Nursing Care: Examining how unconscious biases among healthcare providers may affect care decisions and contribute to health disparities, and developing strategies for mitigation.
- Culturally Competent Care Models: Evaluating the effectiveness of culturally tailored nursing interventions in improving access, engagement, and health outcomes for minority and underserved populations.
- Access to Care for Vulnerable Groups: Investigating barriers to healthcare access (e.g., transportation, insurance, language) for specific vulnerable populations (e.g., homeless individuals, refugees, LGBTQ+ individuals) and the role of nurse navigators.
- Community-Based Participatory Research (CBPR): Utilizing CBPR approaches where nurses collaborate with community members to identify health priorities and co-design interventions to address local health disparities. This collaborative approach is central to many impactful research topics for nursing.
- Policy Advocacy by Nurses for Health Equity: Exploring the role and impact of nurses in advocating for policies that promote health equity at local, state, and national levels.

Choosing research topics for nursing within health equity can contribute to a more just and equitable healthcare system.
8. Palliative and End-of-Life Care Across the Lifespan
Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for patients and families facing serious illness, while end-of-life care focuses on comfort and dignity during the final stages of life. Nurses are central to providing this specialized, compassionate care. This area remains rich with meaningful research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Early Integration of Palliative Care: Investigating the benefits and challenges of integrating palliative care services earlier in the disease trajectory for patients with life-limiting illnesses.
- Communication in Palliative Care: Exploring effective communication strategies for nurses when discussing prognosis, goals of care, and advance care planning with patients and families.
- Symptom Management at End of Life: Evaluating the effectiveness of pharmacological and non-pharmacological nursing interventions for managing complex symptoms like pain, dyspnea, and delirium in terminally ill patients.
- Bereavement Support for Families: Assessing the impact of nurse-led bereavement support programs on the grieving process and well-being of surviving family members.
- Cultural Considerations in End-of-Life Decision Making: Understanding how cultural beliefs and values influence preferences for end-of-life care and how nurses can provide culturally sensitive support. Such research topics for nursing highlight the importance of cultural humility.
9. Infection Prevention and Control in Healthcare Settings
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) pose a significant threat to patient safety and contribute to increased morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. Nurses are critical in implementing and adhering to infection prevention and control (IPC) measures. Thus, IPC offers many vital research topics for nursing.
Potential Research Areas:
- Hand Hygiene Compliance: Investigating innovative strategies and behavioral interventions to improve and sustain hand hygiene compliance among healthcare workers.
- Effectiveness of Isolation Precautions: Evaluating the impact of different types of isolation precautions on HAI rates, patient psychological well-being, and nursing workload.
- Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs: Exploring the role of nurses in promoting appropriate antibiotic use and contributing to antimicrobial stewardship efforts to combat antibiotic resistance. This is an urgent area among research topics for nursing.
- Environmental Cleaning and Disinfection: Assessing the effectiveness of various cleaning protocols and technologies in reducing microbial contamination on surfaces in healthcare settings.
- Nurse Education and Training in IPC: Evaluating the impact of different educational approaches on nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to infection prevention and control. This provides avenues for practical research topics for nursing focused on education.
10. Nursing Education and Professional Development
The quality of nursing care is directly linked to the quality of nursing education and the ongoing professional development of nurses. Research in this area can inform curriculum development, teaching methodologies, and strategies for fostering lifelong learning. This area provides essential research topics for nursing focused on the profession itself.
Potential Research Areas:
- Innovative Teaching Strategies in Nursing Education: Evaluating the effectiveness of simulation-based learning, problem-based learning, and interprofessional education in preparing nursing students for practice.
- Transition to Practice for New Graduate Nurses: Investigating the challenges faced by new nurses and the impact of residency programs and preceptorship models on their competence, confidence, and retention.
- Continuing Education and Competency Maintenance: Assessing the effectiveness of various continuing education modalities in ensuring nurses maintain and enhance their clinical competencies throughout their careers. For those seeking help with research topics for nursing, this area offers many relatable avenues. Nursing Papers is the go-to platform for customized help with nursing research papers, essays, case studies, thesis and dissertations. Our service covers topic suggestion, research paper writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal.
- Leadership Development in Nursing: Exploring effective strategies for identifying and developing nurse leaders at all levels, from charge nurses to executive positions.
- Impact of Clinical Learning Environments: Examining how the characteristics of clinical placement sites and the quality of clinical supervision influence student learning outcomes and their perception of the nursing profession. Exploring these research topics for nursing can enhance the pipeline of skilled nurses.
Navigating Your Research Journey
Choosing from the myriad of potential research topics for nursing is the first step in a challenging yet rewarding journey. Whether you are a DNP student seeking a capstone project or a seasoned researcher looking for your next area of inquiry, the topics outlined above offer fertile ground for investigation. Remember to consider your personal interests, available resources, and the potential impact of your work.
For students or professionals who find the process of refining research topics for nursing or developing a full proposal overwhelming, resources are available. Some may seek mentorship from experienced faculty, while others might explore options such as research paper writing services for guidance on structuring their arguments or polishing their final manuscript after their research is complete. However, the core intellectual work of identifying and pursuing meaningful research topics for nursing remains a personal and professional endeavor.
The advancement of nursing science relies on the curiosity, dedication, and rigor of nurse researchers. By tackling these pressing research topics for nursing, and countless others, nurses can continue to drive improvements in patient care, shape health policy, and elevate the standing of the profession. The future of healthcare is inextricably linked to the insights gained from exploring such crucial research topics for nursing.
As the healthcare landscape continues to shift, the demand for innovative research topics for nursing will only grow, underscoring the vital role of research in this indispensable profession. These research topics for nursing are not exhaustive but represent key areas where nursing research can make a substantial difference. The continuous exploration of new research topics for nursing is essential for the vitality and progress of the nursing field.