Table of Contents
Nursing education is a rigorous yet profoundly rewarding journey, blending intricate theoretical knowledge with demanding practical skills. Central to this educational process are nursing assignments. These tasks are far more than mere academic hurdles; they are carefully designed pedagogical tools meant to cultivate critical thinking, enhance clinical reasoning, deepen understanding of complex health concepts, and ultimately shape competent, compassionate, and effective nursing professionals. For students embarking on or progressing through their nursing studies, understanding the landscape of nursing assignments is crucial for success.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide, delving into the common types of nursing assignments students typically encounter. Furthermore, it provides practical, actionable tips and strategies to not only complete these assignments effectively but also to maximize their learning potential. Mastering these tasks is integral to academic achievement and lays a solid foundation for a successful nursing career. The variety and complexity of nursing assignments reflect the multifaceted nature of the nursing profession itself.
Why Are Nursing Assignments So Important?
Before exploring the specific types, it’s vital to appreciate the fundamental role nursing assignments play in a student’s development:
- Bridging Theory and Practice: Assignments like case studies and care plans directly challenge students to apply theoretical knowledge learned in lectures and textbooks to simulated or real-world patient scenarios.
- Developing Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning: Nursing requires constant analysis, evaluation, and decision-making. Nursing assignments are designed to hone these skills, pushing students to think critically about patient data, potential interventions, and expected outcomes.
- Enhancing Research Skills: Many assignments require students to delve into academic literature, finding, evaluating, and synthesizing evidence to support their arguments or care decisions. This builds foundational skills for evidence-based practice, a cornerstone of modern nursing.
- Improving Communication Skills: Whether through written essays, detailed care plans, or oral presentations, nursing assignments necessitate clear, concise, and professional communication – a skill essential for interacting with patients, families, and interdisciplinary teams.
- Assessing Understanding and Competency: Educators use assignments to gauge student comprehension of course material, their ability to apply concepts, and their readiness for more advanced clinical practice.
- Preparation for Professional Documentation: Tasks like care planning and reflective journaling mirror the documentation practices required in clinical settings, familiarizing students with professional standards and formats.
- Fostering Lifelong Learning: The process of researching, analyzing, and writing for nursing assignments cultivates habits of inquiry and self-directed learning that are essential for staying current in the ever-evolving field of healthcare.
Successfully navigating the diverse range of nursing assignments is therefore not just about grades, but about building the core competencies required of a registered nurse.
Common Types of Nursing Assignments
Nursing programs utilize a variety of assignment formats to assess different skills and knowledge domains. Here are some of the most common types students will encounter:
1. Nursing Essays
- Description: Perhaps the most traditional academic assignment, nursing essays require students to explore a specific topic in depth, develop a clear argument or thesis, and support it with credible evidence from scholarly sources.
- Common Topics: Essays might cover ethical dilemmas in nursing, analyses of nursing theories, discussions of healthcare policies, explorations of specific disease processes or patient populations, or historical perspectives on nursing.
- Skills Developed: Research, critical analysis, argumentation, academic writing, referencing, and the ability to synthesize information from various sources. These foundational nursing assignments build strong writing habits.
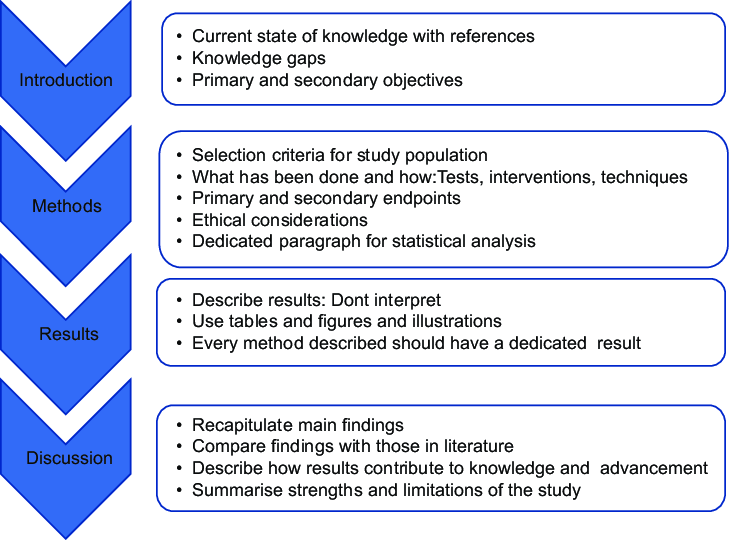
2. Case Studies
- Description: Nursing case studies present students with a detailed scenario, typically involving a fictional or anonymized real patient. Students must analyze the patient’s history, symptoms, and context to develop diagnoses, propose interventions, and predict outcomes.
- Structure: Often includes sections like patient presentation, medical history, assessment findings (subjective and objective data), nursing diagnoses (prioritized), planned interventions with rationales, evaluation criteria, and sometimes a reflection on the case.
- Skills Developed: Clinical reasoning, diagnostic skills, application of the nursing process, problem-solving, critical thinking under simulated clinical pressure, and understanding the holistic nature of patient care. Case study nursing assignments are pivotal for practical application.
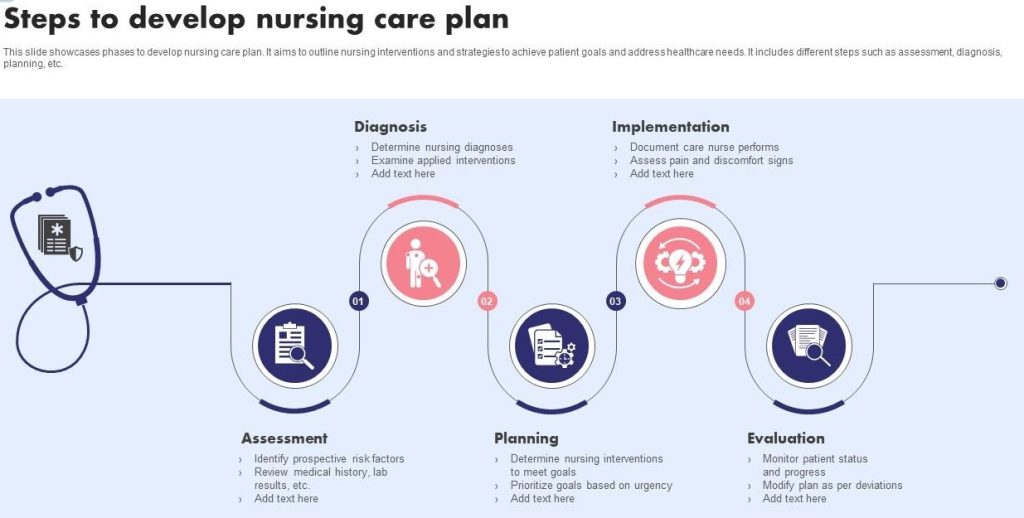
3. Nursing Care Plans
- Description: A cornerstone of nursing practice and education, care plans are systematic documents outlining the nursing care for a specific patient. They require students to utilize the nursing process (Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation – ADPIE).
- Components: Typically involve detailed patient assessment data, formulation of prioritized nursing diagnoses (often using standardized language like NANDA-I), setting measurable patient goals (NOC), selecting appropriate nursing interventions (NIC) with scientific rationales, implementing the plan (often hypothetically in assignments), and defining evaluation methods.
- Skills Developed: Systematic planning, prioritization, application of nursing theory and standardized terminologies, critical thinking about patient needs, goal setting, and understanding the rationale behind nursing actions. These detailed nursing assignments directly mimic professional practice.
4. Research Papers and Literature Reviews
- Description: These nursing assignments require a more extensive investigation into a specific nursing topic. A research paper might involve collecting and analyzing original data (less common at undergraduate levels) or, more typically, conducting a thorough literature review. A literature review synthesizes and critically evaluates existing research on a topic to identify gaps, trends, or consensus.
- Process: Involves formulating a research question, conducting comprehensive searches of academic databases (e.g., CINAHL, PubMed, Scopus), critically appraising selected articles, synthesizing findings, and writing a structured paper according to academic conventions.
- Skills Developed: Advanced research skills, understanding of research methodologies, critical appraisal of evidence, synthesis of complex information, academic writing proficiency, and contribution to the understanding of evidence-based practice.
5. Reflective Journals or Practice Reflections
- Description: Often linked to clinical placements, reflective journals require students to critically reflect on their experiences, observations, and actions in the clinical setting. They connect theoretical learning with practical realities and encourage self-awareness.
- Structure: May follow specific reflective models (e.g., Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle, Johns’ Model of Structured Reflection) guiding students through describing an event, analyzing feelings and thoughts, evaluating the experience, analyzing what was learned, and planning for future practice.
- Skills Developed: Self-assessment, critical reflection, linking theory to practice, emotional intelligence, identifying learning needs, developing professional identity, and ethical reasoning. These personal nursing assignments foster deep learning.
6. Presentations (Oral and Poster)
- Description: Students may be required to present their findings from research, case studies, or group projects to their peers and instructors. This can take the form of an oral presentation (often using slides) or a scientific poster presentation.
- Formats: Can be individual or group-based. Oral presentations require structuring information logically for spoken delivery, while poster presentations emphasize concise visual communication of key information.
- Skills Developed: Public speaking, synthesis of information for different formats, visual communication (slide/poster design), responding to questions, and summarizing complex topics clearly and concisely.
7. Group Projects
- Description: Many nursing programs incorporate group projects to foster teamwork and collaboration, mirroring the interdisciplinary nature of healthcare. These projects can range from joint presentations to collaborative research papers or community health assessments.
- Challenges and Benefits: Require effective communication, task delegation, conflict resolution, and shared accountability. They provide valuable experience in working within a team, a critical skill for nurses.
- Skills Developed: Collaboration, teamwork, communication, negotiation, project management, and shared problem-solving. Managing group dynamics is a key part of these nursing assignments.
8. Concept Maps
- Description: Concept maps are visual tools that help students organize and represent knowledge. They use nodes (concepts) and links (relationships) to illustrate connections between different ideas, such as patient symptoms, underlying pathophysiology, nursing diagnoses, and interventions.
- Application: Often used to understand complex patient conditions or to visually structure a care plan.
- Skills Developed: Critical thinking, synthesis of information, identifying relationships between concepts, visual learning, and holistic understanding of patient situations. These visual nursing assignments aid comprehension.
9. Clinical Skills Checklists and Evaluations
- Description: While not traditional written assignments, performance evaluations during clinical labs or placements, often using detailed checklists, function as practical nursing assignments. Students must demonstrate competency in performing specific nursing procedures (e.g., medication administration, wound care, physical assessment).
- Assessment: Based on direct observation by clinical instructors against established standards of practice and safety protocols.
- Skills Developed: Psychomotor skills, adherence to protocols, patient safety practices, communication during procedures, and integration of theoretical knowledge into hands-on practice.
Understanding this variety helps students anticipate what to expect and begin developing the versatile skill set needed to tackle different types of nursing assignments.
Success Tips for Tackling Nursing Assignments
Excelling in nursing assignments requires more than just understanding the content; it demands strategic planning, effective study habits, and meticulous execution. Here are key tips for success:
1. Deconstruct the Prompt and Understand Requirements
- Read Carefully: Don’t just skim the assignment brief. Read it multiple times, highlighting keywords, specific questions to be answered, required sections, word count limits, and the submission deadline.
- Identify the Core Task: What type of assignment is it (essay, case study, care plan)? What is the main objective? Are you asked to analyze, compare, evaluate, reflect, or apply?
- Consult the Marking Rubric: This is your roadmap to a good grade. Understand how points are allocated. Pay close attention to areas with high weightage. The rubric clarifies the specific expectations for your nursing assignment.
- Clarify Doubts: If anything is unclear, ask your instructor or teaching assistant for clarification well before the deadline. Don’t make assumptions.
2. Master Time Management and Planning
- Start Early: Procrastination is the enemy of quality work, especially for complex nursing assignments. Starting early provides ample time for research, thinking, drafting, and revising.
- Break It Down: Divide the assignment into smaller, manageable steps (e.g., research, outline, draft introduction, draft body paragraphs, draft conclusion, referencing, proofreading).
- Create a Timeline: Allocate specific deadlines for each step. Work backward from the final submission date. Use a calendar or planner to track your progress.
- Allocate Sufficient Time: Be realistic about how long each step will take. Research and writing often take longer than anticipated. Factor in time for unexpected delays.
3. Develop Effective Research Strategies
- Utilize Library Resources: Become proficient in using nursing-specific databases like CINAHL, PubMed, Medline, and Scopus. Librarians are excellent resources for learning effective search strategies.
- Focus on Credible Sources: Prioritize peer-reviewed journals, reputable nursing organizations, government health agencies, and academic textbooks. Be cautious with websites; look for established, credible sources (.gov, .edu, .org from known health bodies).
- Evaluate Evidence Critically: Don’t just accept information at face value. Consider the study methodology, sample size, potential biases, and relevance to your topic. Is the evidence current?
- Organize Your Research: Use reference management software (e.g., EndNote, Zotero, Mendeley) or a systematic method (like a spreadsheet or annotated bibliography) to keep track of sources, key findings, and quotes. This is crucial for complex nursing assignments.
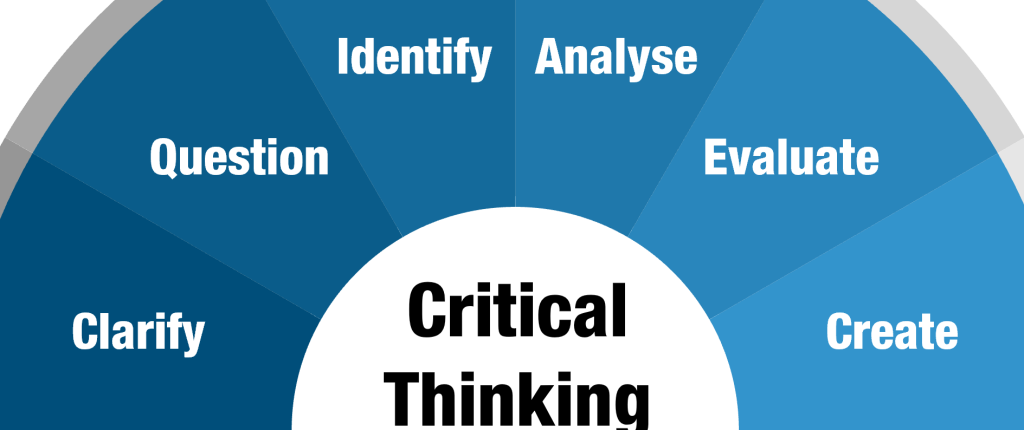
4. Engage in Critical Thinking and Analysis
- Go Beyond Description: Don’t just summarize information. Analyze it, interpret it, question it, and connect it to broader nursing concepts or patient care principles.
- Ask Why: Constantly ask “why” – why is this assessment finding significant? Why is this intervention appropriate? Why did this outcome occur?
- Connect Theory to Practice: Explicitly link theoretical concepts, nursing models, or research findings to the practical aspects of your assignment (e.g., the patient scenario in a case study).
- Consider Multiple Perspectives: Explore different viewpoints or potential approaches, especially in essays dealing with ethical or policy issues.
5. Focus on Strong Writing, Structure, and Clarity
- Develop a Clear Outline: Before writing, create a logical structure for your assignment. This ensures a coherent flow of ideas.
- Craft a Strong Introduction: Clearly state the purpose of your assignment and provide a roadmap for the reader. Include a thesis statement if applicable (especially for essays).
- Use Clear Topic Sentences: Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea, introduced by a clear topic sentence.
- Maintain Academic Tone: Use formal language, objective phrasing (unless it’s a reflection), and precise nursing terminology. Avoid slang, contractions, and overly casual language.
- Ensure Cohesion and Flow: Use transition words and phrases to connect ideas smoothly between sentences and paragraphs.
- Write a Concise Conclusion: Summarize the main points and reiterate the significance of your findings or arguments. Don’t introduce new information.
6. Adhere Meticulously to Formatting and Referencing
- Know Your Style Guide: Most nursing programs use APA (American Psychological Association) style, but always confirm the required format. Obtain the latest edition of the style manual.
- Consistency is Key: Apply formatting rules consistently throughout the paper (e.g., font, margins, spacing, headings, title page).
- Master In-Text Citations and Reference Lists: Cite every source properly both within the text and in the final reference list. Errors here can lead to accusations of plagiarism and significant grade deductions. These details matter in nursing assignments.
- Utilize Tools (Carefully): Reference management software can help format citations and bibliographies, but always double-check their output for accuracy against the style guide.
7. Prioritize Proofreading and Editing
- Don’t Skip This Step: Even excellent content can be undermined by errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, and syntax.
- Take a Break: Step away from your completed draft for a day or two before proofreading. Fresh eyes catch more errors.
- Read Aloud: Reading your work aloud helps identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and other errors that your eyes might miss.
- Proofread Methodically: Check for one type of error at a time (e.g., first spelling, then punctuation, then grammar, then referencing).
- Get a Second Opinion: Ask a classmate, friend, or writing center tutor to read your draft. They may spot errors or areas needing clarification that you overlooked. Careful editing is essential for polished nursing assignments.
8. Leverage Available Resources
- Instructors and TAs: They are your primary resource. Attend office hours, ask questions in class, and seek feedback on drafts if permitted.
- Academic Writing Centers: Most universities offer writing support services. Tutors can help with structure, clarity, grammar, and referencing – invaluable help for challenging nursing assignments.
- Library Staff: Librarians are experts in research strategies and accessing credible information.
- Peer Study Groups: Discussing assignments with peers can clarify concepts and generate ideas, but ensure all submitted work is your own.
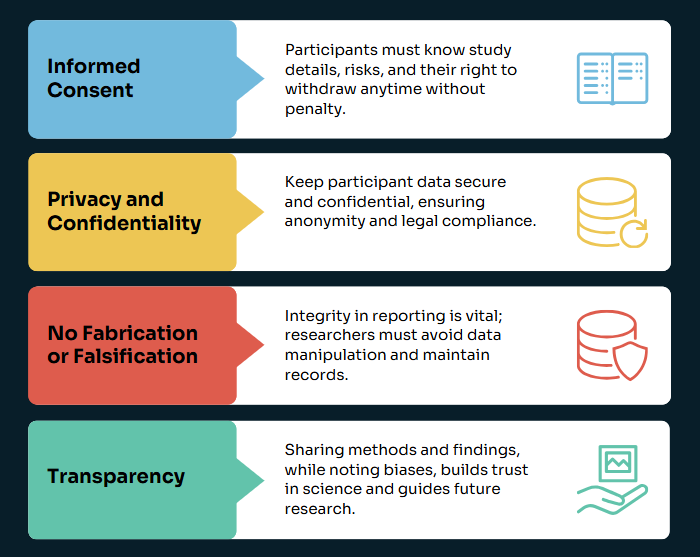
9. Maintain Academic Integrity
- Understand Plagiarism: Know what constitutes plagiarism (copying text, improper paraphrasing, submitting work done by others) and its serious consequences.
- Cite Everything: When in doubt, cite your source. Proper citation gives credit to original authors and strengthens your own work.
- Protect Patient Confidentiality: When using real clinical experiences (e.g., in reflections or anonymized case studies), strictly adhere to HIPAA or relevant privacy regulations. Use pseudonyms and omit identifying details.

10. Know When and How to Seek Help
- Acknowledge Challenges: Nursing school is demanding. It’s okay to find certain nursing assignments difficult or overwhelming.
- Proactive Communication: If you’re struggling, communicate with your instructor early. Don’t wait until the deadline is looming. They may offer extensions (under valid circumstances) or guidance.
- Utilize Institutional Support: Explore resources like tutoring services, counseling centers (for managing stress), and academic skills workshops offered by your university.
- Consider External Support Ethically: Some students may feel they need additional support beyond institutional resources. While searching for “help with nursing assignments” online, students might encounter various services. Options like nursing assignment help or specialized nursing assignment writing services exist. If you are feeling overwhelmed, get professional help with nursing assignments from Nursing Papers. We can help you with topic suggestion, nursing assignments writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Besides nursing assignments, we also help students to write essays, research papers, term papers, case studies, thesis and dissertations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Challenge
Nursing assignments are integral components of nursing education, designed to build the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities essential for safe and effective practice. While they can be challenging and time-consuming, approaching them strategically and diligently transforms them from mere requirements into valuable learning opportunities.
By understanding the different types of nursing assignments, deconstructing requirements, managing time effectively, honing research and writing skills, thinking critically, paying meticulous attention to detail, and utilizing available resources, nursing students can not only succeed academically but also build a strong foundation for their future careers. Remember that each nursing assignment completed is a step closer to becoming a knowledgeable, skilled, and compassionate nurse, ready to make a positive impact on patients’ lives. Embrace the challenge, learn from the process, and leverage every nursing assignment to grow as a future healthcare professional. The effort invested in mastering these nursing assignments today pays dividends in competence and confidence tomorrow.