Table of Contents
Pediatric nursing is a field steeped in both scientific rigor and the profound impact of human connection. Research within this domain holds immense potential to improve the lives of children and their families, from developing innovative interventions to advocating for equitable access to healthcare. Crafting a compelling research paper on pediatric nursing requires a skillful blend of clarity, depth, and empathy.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip aspiring authors with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the complex process of writing a research paper. The insights discussed in this guide will enable you to craft a pediatrics nursing research paper that not only informs but also inspires meaningful action.
Steps to Crafting a Stellar Pediatric Nursing Research Paper
1. Choosing a Compelling Topic:
The foundation of a successful research paper lies in selecting a topic that is both relevant and resonates with your personal interests. Pediatric nursing encompasses a vast array of disciplines, from acute care to community health, each offering unique avenues for exploration. Consider your own experiences, current trends in the field, and potential knowledge gaps that need addressing.
Think critically about your chosen topic:
- Relevance: Is your topic addressing a current and pressing issue within pediatric nursing?
- Impact: Will your research contribute to improved patient care or advocate for policy changes?
- Feasibility: Do you have access to the necessary resources and data to conduct a thorough investigation?
Examples of potential research paper topics in pediatric nursing:
- Addressing pain management in children with chronic illnesses: This topic could explore the effectiveness of different pain relief strategies, cultural considerations in pain perception, or the impact of pain on child development.
- Improving communication strategies between nurses and families in critical care settings: This topic could delve into strategies for facilitating open dialogue, addressing family anxieties, or promoting shared decision-making.
- Evaluating the impact of play therapy on the psychological well-being of children undergoing chemotherapy: This topic could examine the role of play in coping with cancer treatment, reducing stress and anxiety, or promoting a sense of normalcy.
- Developing culturally-sensitive interventions for children with developmental disabilities: This topic could focus on addressing cultural differences in healthcare access, promoting family involvement, or empowering children to advocate for their needs.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of telemedicine in providing pediatric nursing care in remote areas: This topic could explore the challenges and benefits of using technology to deliver healthcare services, improving access and reducing disparities.
2. Conducting a Thorough Literature Review:
The bedrock of a strong research paper lies in a comprehensive understanding of existing knowledge. A meticulous literature review is not simply a list of citations. Instead, it is a critical analysis of relevant research findings, identifying gaps, and formulating your research question.
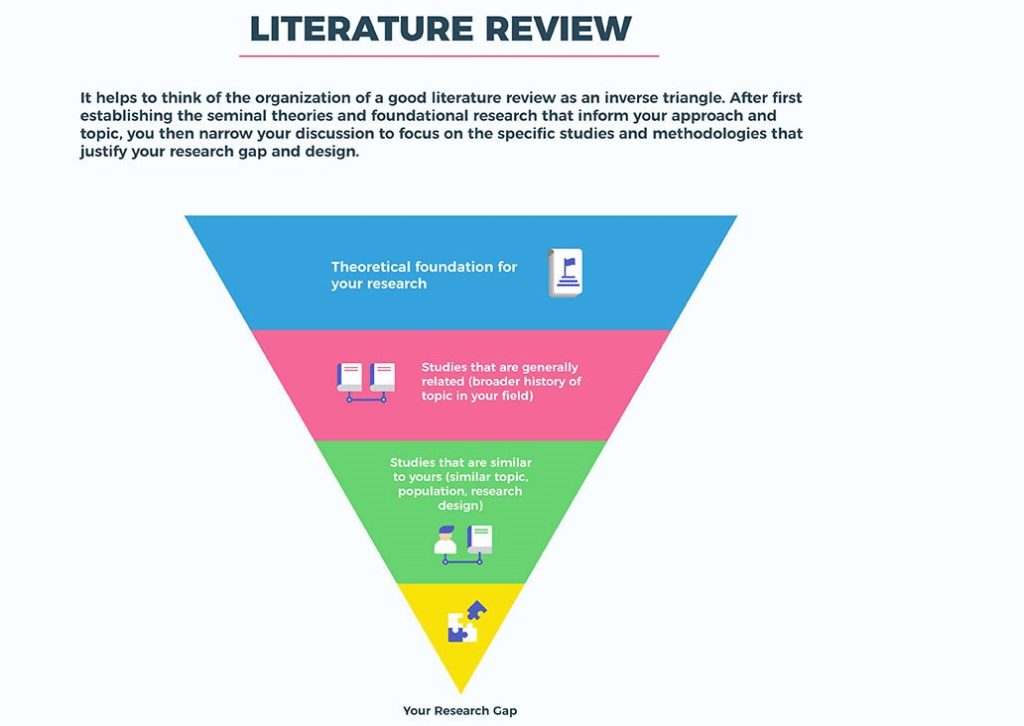
Key steps in conducting a thorough literature review:
- Define your search terms: Choose keywords relevant to your chosen topic and use a combination of terms to refine your search results. For example, searching for “pain management” and “pediatric oncology” will yield more specific results compared to a broad search for “pain management in children.”
- Utilize databases and online resources: Leverage specialized databases such as CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature) and PubMed, which offer a vast collection of peer-reviewed articles related to nursing research.
- Evaluate sources critically: Assess the credibility of sources, considering the journal’s reputation, author’s credentials, and the research methodology employed.
- Synthesize findings: Identify key themes, emerging trends, and areas of controversy within the literature.
- Identify knowledge gaps: Analyze the existing research to pinpoint areas where further investigation is necessary.
3. Formulating a Strong Research Question:
A well-defined research question serves as the compass guiding your research journey. It should be clear, concise, and specific enough to allow for a focused and meaningful investigation.
Characteristics of a strong research question:
- Specific: It focuses on a narrow aspect of the chosen topic.
- Measurable: It can be tested and analyzed using quantifiable data.
- Achievable: It can be investigated with available resources and timeframes.
- Relevant: It addresses a significant issue in pediatric nursing.
- Time-bound: It has a clear timeframe for completion.
Example of a strong research question related to pediatric oncology nursing:
- Does a structured art therapy program improve the quality of life and emotional well-being of children undergoing chemotherapy treatment compared to standard care?
4. Crafting a Compelling Methodology:
The methodology section outlines the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques employed in your study. This section needs to be detailed, transparent, and defensible to ensure the reliability and validity of your findings.
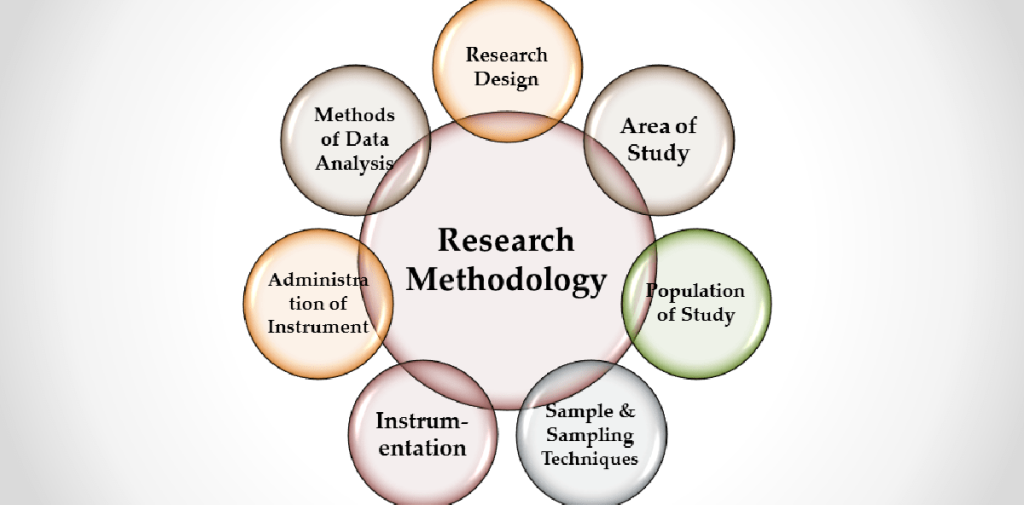
Key elements of a strong methodology section:
- Research design: Clearly define the type of research (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods) and explain its suitability for addressing your research question.
- Data collection methods: Describe the instruments used to gather data (questionnaires, interviews, observations), the sample size, and the participant selection criteria.
- Data analysis techniques: Explain the statistical tests or qualitative analysis methods used to interpret and analyze the data collected.
- Ethical considerations: Address the ethical implications of your research, including informed consent, data privacy, and participant confidentiality.
5. Presenting the Results with Clarity and Precision:
The results section presents the findings of your research in a clear, organized, and objective manner. Avoid unnecessary jargon and use tables, figures, and graphs to visually represent the data effectively.
Key considerations for presenting results:
- Organization: Structure the results section logically, following the order of your research questions or hypotheses.
- Clarity: Use plain language to describe the data and avoid overly technical terminology.
- Visual aids: Employ graphs, tables, and figures to present complex data in an easily digestible format.
- Objectivity: Present the findings without bias or interpretation.
- Limitations: Acknowledge any limitations of your study, such as sample size or data collection methods.
6. Discussing the Implications and Significance:
The nursing research paper discussion section goes beyond presenting the data to interpret its meaning, drawing connections to existing research, and exploring the implications of your findings.
Key aspects of a strong discussion section:
- Interpretation of results: Explain the meaning of your findings and how they relate to your research questions.
- Comparison with existing literature: Discuss how your findings align with or contradict existing research in the field.
- Implications for practice: Explain how your findings can be applied to improve pediatric nursing care, education, or research.
- Limitations: Reiterate the limitations of your study and suggest avenues for future research.
- Significance: Emphasize the contribution of your research to the advancement of knowledge and practice in pediatric nursing.
7. Writing a Convincing Conclusion:
The conclusion summarizes the key findings, restates the significance of your research, and provides a call to action. It should leave a lasting impression on the reader and inspire them to engage with the topic further.
Elements of a strong conclusion:
- Reiterate key findings: Briefly restate the major findings of your study and their relevance to the research question.
- Highlight significance: Emphasize the importance of your findings for improving pediatric nursing practice, policy, or education.
- Call to action: Suggest future research directions, advocacy efforts, or practical applications based on your findings.

8. Incorporating Engaging Writing Techniques:
While scientific accuracy is paramount, writing a compelling research paper requires engaging with the reader on an intellectual and emotional level.
Strategies for engaging writing in pediatric nursing research:
- Use a narrative voice: Weave personal anecdotes or case studies to illustrate the human impact of your research.
- Incorporate vivid imagery: Use descriptive language to create a sense of immediacy and connect the reader to the research topic.
- Emphasize the patient perspective: Acknowledge the unique experiences and perspectives of children and families affected by the issue you are researching.
- Tell a compelling story: Structure your paper to create a narrative arc, leading the reader through a journey of discovery and understanding.
9. Seeking Peer Review and Feedback:
Before submitting your paper, it is crucial to seek feedback from peers and mentors within the field. Peer review can identify weaknesses, refine arguments, and improve the overall clarity and impact of your work.
Benefits of peer review:
- Objectivity: Peers provide an unbiased perspective on the strengths and weaknesses of your paper.
- Constructive criticism: Peers offer specific and actionable feedback for improvement.
- Enhanced clarity: Peers can identify areas where your arguments need further clarification or elaboration.
- Improved writing quality: Peers can help refine the flow, language, and overall readability of your paper.
10. Choosing the Right Journal for Publication:
Selecting the appropriate journal for publication is crucial for reaching your target audience and maximizing the impact of your research.
Factors to consider when choosing a journal:
- Scope and focus: Ensure the journal aligns with the specific area of pediatric nursing you are researching.
- Impact factor: Consider the journal’s impact factor, which reflects the average number of citations received by articles published in that journal.
- Audience: Identify the journal’s readership and ensure it aligns with your target audience.
- Submission guidelines: Carefully review the journal’s submission guidelines and ensure your paper meets all the necessary requirements.
11. Ethical Considerations in Pediatric Nursing Research:
Conducting ethical research with vulnerable populations like children is paramount. It requires adhering to strict ethical guidelines and principles.
Key ethical considerations in pediatric nursing research:
- Informed consent: Obtain informed consent from parents or legal guardians before involving children in research.
- Child assent: Involve children in the decision-making process whenever possible, respecting their autonomy and right to participate.
- Confidentiality: Ensure the privacy and confidentiality of all participants, particularly children, protecting their sensitive information.
- Minimizing risk: Design research studies to minimize any potential risks to participants, including physical, psychological, and emotional harm.
- Beneficence: Ensure that research benefits participants or contributes to the advancement of knowledge and practice in pediatric nursing.
Examples of Successful Research Papers on Pediatric Nursing
- “The Impact of Parental Anxiety on Child’s Pain Perception During Chemotherapy” – This paper could explore the relationship between parental anxiety levels and the child’s self-reported pain intensity, contributing to the development of evidence-based interventions for managing pain in pediatric oncology patients.
- “Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Play Therapy Intervention to Reduce Anxiety in Children Undergoing Surgery” – This research could demonstrate the benefits of play therapy in mitigating anxiety in children undergoing surgical procedures, promoting a more holistic approach to pediatric healthcare.
- “Exploring the Experiences of Adolescent Mothers in Accessing Healthcare for their Infants” – This qualitative study could illuminate the unique challenges faced by adolescent mothers in navigating the healthcare system, leading to the development of culturally sensitive interventions and support programs.
Resources for Pediatric Nursing Researchers
- National Institute of Nursing Research (NINR): Provides funding and resources for nursing research, including pediatric nursing.
- Pediatric Nursing Society (PNS): Offers educational resources, networking opportunities, and support for pediatric nurses.
- American Nurses Association (ANA): Provides guidance and resources for nurses, including ethical guidelines for research.
- Sigma Theta Tau International (STTI): A nursing honor society that offers grants and mentorship opportunities for nurse researchers.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): Offers funding opportunities for research projects across various disciplines, including pediatric nursing.
Mistakes to Avoid in a Pediatric Nursing Research Paper
1. Lack of Clarity in Research Question:
A clear and focused research question is crucial for any pediatric nursing research paper. Avoid vague or overly broad questions. Instead, ensure your question is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This will guide your research and make your findings more meaningful.
2. Inadequate Literature Review:
A thorough literature review is essential for understanding the current state of knowledge in pediatrics. It helps identify gaps in the research, provides a foundation for your study, and justifies the need for your research. Make sure your literature review is comprehensive and includes relevant studies, theories, and frameworks related to pediatric nursing.
3. Sampling Bias:
When selecting participants for your research, carefully consider potential sources of bias. Ensure your sample is representative of the target population. This is particularly important in pediatric nursing, where factors such as age, developmental stage, and specific health conditions can influence the results.
4. Ethical Considerations:
Research involving children requires strict adherence to ethical guidelines. Seek informed consent from parents or guardians, and ensure the well-being and confidentiality of the children involved. Ethical considerations are paramount in pediatric nursing research, as children are particularly vulnerable.
5. Lack of Rigorous Methodology:
A well-designed methodology is crucial for obtaining valid and reliable results. Clearly describe your research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. Ensure your research methods are appropriate for the specific topic and population of your pediatric nursing research.
6. Weak Data Analysis and Interpretation:
Thorough data analysis and interpretation are essential for drawing meaningful conclusions from your research. Employ appropriate statistical techniques to analyze your data, and interpret the findings in the context of your research question and existing literature.
7. Poor Writing and Presentation:
A research paper should be written in a clear, concise, and professional manner. Avoid jargon and technical language that might be difficult for readers to understand. Use appropriate formatting and referencing, and ensure the paper flows logically from introduction to conclusion.
8. Lack of Practical Implications:
While pediatric nursing research should be academically rigorous, it should also have practical implications for the field. Discuss how your findings can be used to improve pediatric nursing practice, education, or research.
9. Ignoring the Unique Needs of Children:
Remember that children are not simply small adults. They have unique developmental needs, physical and emotional vulnerabilities, and specific health concerns. Pediatric nursing research must acknowledge these differences and tailor its focus accordingly.
10. Failure to Share Findings:
After completing your research, make sure to disseminate your findings to the broader pediatric nursing community. Publish your research in peer-reviewed journals, present it at conferences, or share it with colleagues and organizations. Sharing your work contributes to the advancement of the field and helps improve the care provided to children.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can increase the quality and impact of your pediatric nursing research paper. It’s essential to ensure your research is rigorous, ethical, and relevant to the needs of children and the practice of pediatric nursing.
Writing a compelling research paper on pediatric nursing demands a meticulous approach, blending scientific rigor with compassionate storytelling. By adhering to the guidelines outlined in this guide, aspiring authors can navigate the complex process of research, effectively communicate their findings, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and practice in pediatric nursing.
Remember, your research has the potential to impact the lives of children and families, making a real difference in the world. Incorporating the principles and strategies highlighted in this guide can enable researchers to write engaging, impactful, and ethically sound research papers on pediatric nursing, ultimately contributing to a brighter future for children and their families.
Get Professional Help with a Research Paper on Pediatric Nursing
While writing a stellar research paper on pediatric nursing can seem daunting, it does not have to be so. At Nursing Papers, we offer professional research paper writing help to enable you get through the task seamlessly. Our service covers topic suggestion, research paper writing, proof reading, formatting and plagiarism removal. Besides, our writers can also help you with crafting original and engaging nursing essays, case studies, dissertations and theses.