Table of Contents
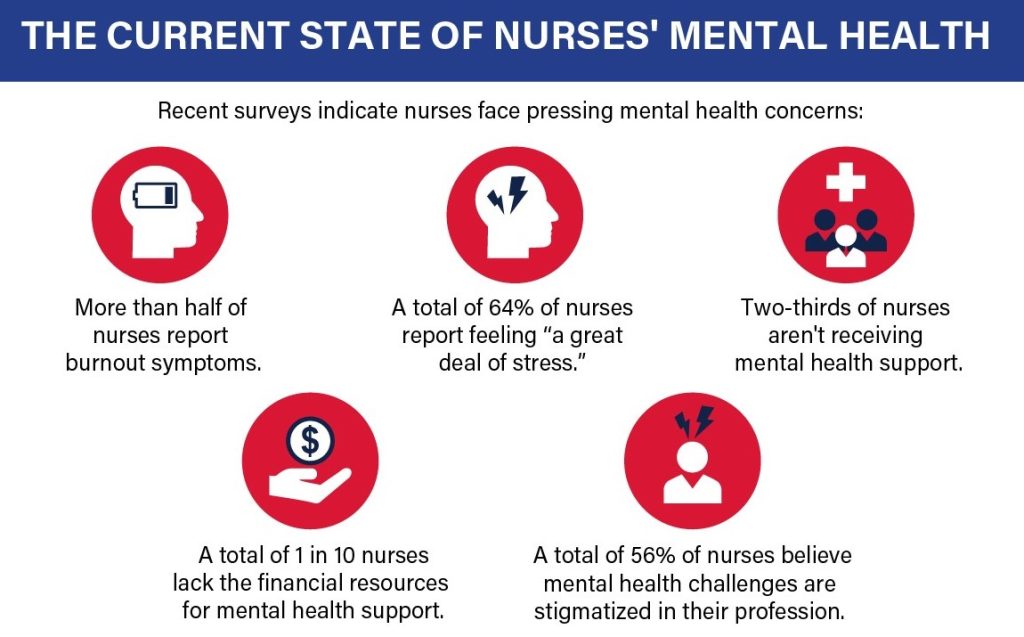
Nurse burnout is a critical issue plaguing healthcare systems worldwide, exacting a heavy toll on the well-being of nursing professionals, the quality of patient care, and the stability of healthcare organizations. Understanding the multifaceted nature of this phenomenon is paramount to developing effective interventions. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of nurse burnout, emphasizing the profound insights that can be gleaned from a case study on nurse burnout. We will explore its dimensions, drivers, and the power of qualitative research, specifically the case study on nurse burnout, to illuminate the lived experiences of nurses.
Deconstructing the Case Study on Nurse Burnout
To effectively utilize and interpret a case study on nurse burnout, one must first understand the core components of burnout and its primary instigators.
- The Three Core Dimensions of Burnout:
- Emotional Exhaustion: This is the feeling of being emotionally overextended and depleted of one’s emotional resources. Nurses experiencing this may feel they have nothing left to give.
- Depersonalization (Cynicism): This involves developing a detached, callous, or excessively cynical attitude towards patients, colleagues, and the work itself. It’s often a coping mechanism to distance oneself from overwhelming emotional demands.
- Reduced Personal Accomplishment: This refers to a feeling of incompetence and a lack of achievement and productivity at work. Nurses may feel their efforts make no difference, leading to a decline in motivation and self-esteem.
- Key Contributing Factors (Drivers):
- Workload and Staffing Ratios: Consistently high patient-to-nurse ratios, excessive overtime, and unmanageable workloads are primary drivers.
- Lack of Control and Autonomy: Limited input into scheduling, patient care decisions, or work processes can lead to feelings of powerlessness.
- Insufficient Support: This includes inadequate support from managers, a lack of peer collegiality, and insufficient resources (e.g., equipment, ancillary staff).
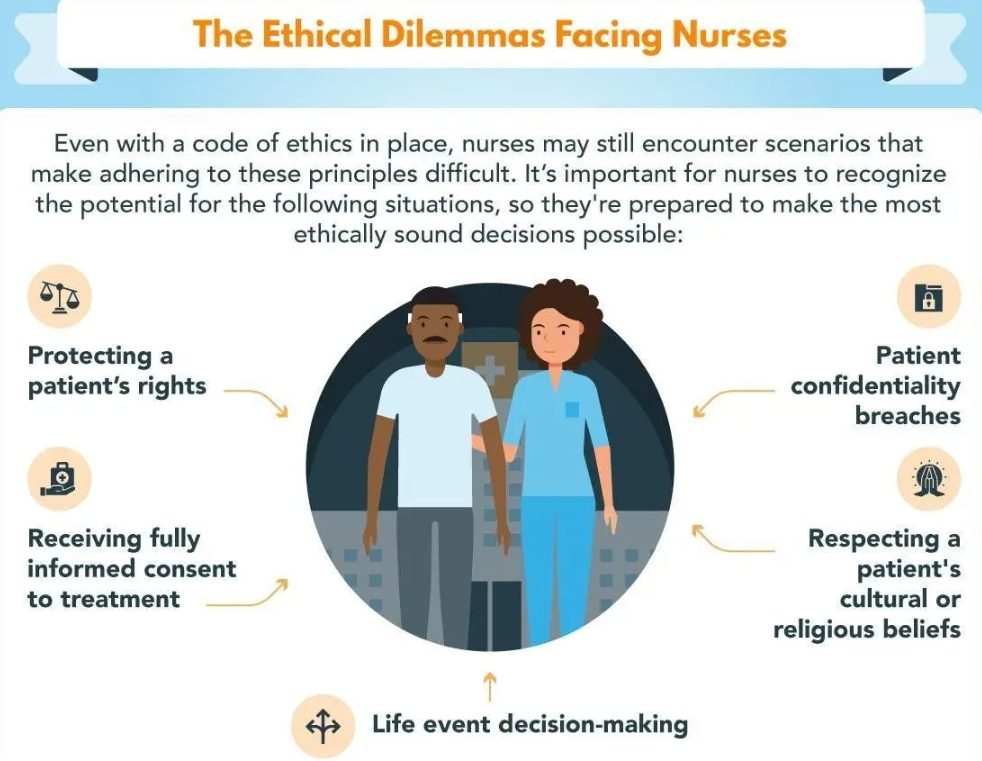
- Moral Distress and Ethical Dilemmas: Being unable to act according to one’s ethical judgment due to institutional constraints causes significant internal conflict.
- Work-Life Imbalance: Difficulty in detaching from work, long or irregular hours, and the emotional toll of nursing can intrude on personal life.
- Organizational Culture: A punitive environment, lack of recognition, poor communication, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize staff well-being contribute significantly.
- Exposure to Trauma and Suffering: Nurses are routinely exposed to human suffering, death, and traumatic events, which can accumulate over time.
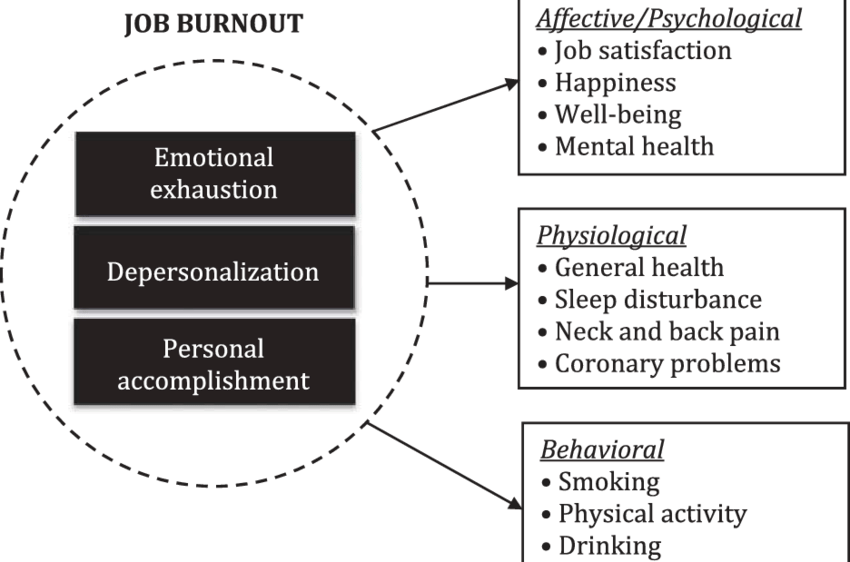
Understanding these dimensions and drivers is absolutely foundational for framing the research questions and analysis plan of any robust case study on nurse burnout.
The Importance of a Case Study on Nurse Burnout
A case study is an in-depth, intensive investigation of a single individual, group, event, or community. In the context of nurse burnout, it allows researchers to explore the phenomenon in its real-life setting, capturing the complexity and richness of individual experiences. The power of a case study on nurse burnout lies in its ability to answer “how” and “why” questions.
- Advantages of using a case study on nurse burnout methodology:
- In-depth Understanding: It provides a holistic and comprehensive understanding of the burnout experience from the nurse’s perspective, capturing nuances that broad surveys might miss.
- Contextual Richness: Burnout doesn’t occur in a vacuum. A case study on nurse burnout examines the specific environmental, organizational, and personal factors influencing an individual’s experience.
- Exploring Lived Experiences: It gives voice to nurses, allowing them to share their stories, struggles, and coping mechanisms in detail. This narrative element is crucial for humanizing the issue.
- Generating Hypotheses: Insights from a detailed case study on nurse burnout can lead to the development of new theories or hypotheses that can then be tested in larger-scale quantitative studies.
- Informing Interventions: By understanding the specific pathways to burnout for individuals in particular settings, targeted and more effective interventions can be designed.
A well-executed case study on nurse burnout moves beyond statistics to tell a compelling story, offering profound insights that can drive meaningful change. The very nature of a focused case study on nurse burnout allows for a deep dive into these personal narratives.
Designing an Effective Nurse Burnout Case Study
The quality of insights derived from a case study on nurse burnout is directly dependent on the rigor of its design. Careful planning is essential.
- Defining the Scope and Research Questions:
- The first step is to clearly define what the case study on nurse burnout aims to investigate. Research questions should be specific and focused.
- Examples:
- “How do ICU nurses experience and cope with moral distress leading to burnout in a high-acuity urban hospital?”
- “What are the key organizational factors contributing to burnout among new graduate nurses in their first year of practice, as explored through a case study on nurse burnout?”
- “This case study on nurse burnout will explore the impact of leadership styles on team burnout in a long-term care facility.”
- Participant Selection (The “Case”):
- Single Case vs. Multiple Case Design: A single case study on nurse burnout provides deep insight into one unique situation, while a multiple case design allows for comparison and contrast across different contexts, potentially leading to more generalizable findings.
- Criteria for Selection: Participants should be chosen purposefully. Criteria might include years of experience, specialty, self-reported burnout symptoms, or working in a specific high-risk environment. The selection process is critical for the relevance of the case study on nurse burnout.
- Data Collection Methods for a Case Study on Nurse Burnout:
- A key strength of the case study method is its ability to utilize multiple sources of evidence. For a case study on nurse burnout, these may include:
- In-depth Interviews: Semi-structured or unstructured interviews are often the primary data source, allowing nurses to share their experiences in their own words.
- Observations: Observing nurses in their work environment (with consent) can provide contextual data about workload, team dynamics, and stressors.
- Document Analysis: Reviewing reflective journals, performance reviews (anonymized), incident reports, or relevant hospital policies can offer additional layers of understanding.
- Surveys/Questionnaires: Standardized burnout measures (e.g., Maslach Burnout Inventory – MBI) can be used as supplementary data to quantify aspects of the burnout experience within the case study on nurse burnout.
- A key strength of the case study method is its ability to utilize multiple sources of evidence. For a case study on nurse burnout, these may include:
- Ethical Considerations in a Case Study on Nurse Burnout:
- Given the sensitive nature of burnout, ethical considerations are paramount when conducting any case study on nurse burnout.
- Informed Consent: Participants must fully understand the purpose of the study, how their data will be used, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Confidentiality and Anonymity: Protecting the identity of participants and their institutions is crucial. Pseudonyms and de-identification of data are standard practices.
- Minimizing Harm and Providing Support: Discussing burnout can be emotionally taxing. Researchers must be sensitive, prepared to pause or stop if a participant becomes distressed, and have information on support services available.
- Data Storage and Security: Secure storage of sensitive data collected for the case study on nurse burnout is essential.
- Given the sensitive nature of burnout, ethical considerations are paramount when conducting any case study on nurse burnout.
The rigor of a case study on nurse burnout relies heavily on this meticulous design phase, ensuring that the data collected is rich, relevant, and ethically sound.
Analyzing and Interpreting Data from the Case Study
Once data collection is complete, the next critical phase is analysis and interpretation. Qualitative data analysis is an iterative process aimed at identifying patterns, themes, and meanings within the collected information.
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques:
- Thematic Analysis: This is one of the most common approaches. It involves systematically identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within the data. For a case study on nurse burnout, themes might relate to workload, support, coping strategies, etc.
- Narrative Analysis: This focuses on the stories people tell, examining how they construct their experiences of burnout.
- Content Analysis: This can involve quantifying the frequency of certain words or concepts within interview transcripts or documents, although it’s often used in conjunction with more interpretive thematic approaches in a case study on nurse burnout.
- Identifying Key Themes and Patterns:
- The researcher immerses themselves in the data (e.g., reading interview transcripts multiple times, reviewing observation notes).
- Initial codes are generated, which are then grouped into broader themes.
- The central question is: What recurring issues, experiences, and perceptions emerge from the case study on nurse burnout data?
- Ensuring Trustworthiness (Validity and Reliability in Qualitative Research):
- Qualitative research uses different criteria than quantitative research to establish rigor. These include:
- Credibility: Ensuring the findings accurately reflect the participants’ experiences (e.g., through member checking, where participants review findings).
- Transferability: The extent to which findings from the case study on nurse burnout can be applied to other contexts (achieved through rich, thick descriptions).
- Dependability: The consistency of findings if the study were repeated under similar conditions (e.g., through an audit trail).
- Confirmability: Ensuring findings are based on the data, not researcher bias (e.g., through reflexivity, where researchers acknowledge their own biases).
- Triangulation: Using multiple data sources (e.g., interviews, observations, documents) to corroborate findings is a key strategy for enhancing the trustworthiness of a case study on nurse burnout.
- Qualitative research uses different criteria than quantitative research to establish rigor. These include:
- Drawing Meaningful Conclusions:
- The final step is to synthesize the themes and interpret what they mean in relation to the research questions and existing literature on nurse burnout.
- What does this specific case study on nurse burnout teach us about the individual’s journey, the contributing factors in their specific environment, and potential points for intervention?
Illustrative Examples: Exploring Different Facets Through a Case Study
To better understand the practical application and insights, let’s consider a few hypothetical scenarios. Each of these scenarios could form the basis of an in-depth case study on nurse burnout.
- Hypothetical Case Study on Nurse Burnout 1: Sarah, the ICU Veteran
- Background: Sarah, 45, has been an ICU nurse for 18 years. She is highly skilled but has witnessed countless traumatic events, faced chronic understaffing, and dealt with complex ethical dilemmas regarding end-of-life care.
- Presenting Symptoms: Emotional numbness, a growing cynicism towards new hospital initiatives (seeing them as “more pointless work”), difficulty sleeping, and persistent physical fatigue. She feels detached from her patients, a stark contrast to her earlier empathy.
- Key Insights from this type of case study on nurse burnout: This case study on nurse burnout could highlight the impact of cumulative trauma, compassion fatigue, moral distress, and the erosion of idealism over a long career in a high-stress environment. It might explore how systemic issues like staffing and lack of psychological support contribute to the burnout of experienced, valuable nurses.
- Hypothetical Case Study on Nurse Burnout 2: David, the New Graduate in Med-Surg
- Background: David, 24, is six months into his first nursing job on a busy medical-surgical unit. He often feels overwhelmed by his patient load, receives inconsistent support from his preceptor (who is also overworked), and struggles with time management and complex patient needs.
- Presenting Symptoms: High anxiety before shifts, frequent feelings of incompetence, difficulty asking for help for fear of appearing incapable, and thoughts of leaving the nursing profession altogether.
- Key Insights from this case study on nurse burnout: Such a case study on nurse burnout would likely underscore the challenges of “reality shock” for new graduates, the critical importance of effective onboarding, robust mentorship programs, and manageable workloads during the transition to practice. It could explore the specific vulnerabilities of new nurses to burnout.
- Hypothetical Case Study on Nurse Burnout 3: Maria, the Nurse Manager Facing Staff Shortages
- Background: Maria, 52, is a nurse manager for an oncology unit. She is constantly battling staff shortages, trying to cover shifts, advocating (often unsuccessfully) for more resources, and supporting her team who are themselves struggling with burnout and moral distress.
- Presenting Symptoms: Chronic frustration, guilt over not being able to adequately support her staff, sleep disturbances, difficulty delegating (as there’s no one to delegate to), and feeling caught between the demands of upper management and the needs of her team.
- Key Insights from this case study on nurse burnout: This case study on nurse burnout would illuminate the unique pressures faced by nurse leaders, the concept of “second-hand” or vicarious burnout from managing a distressed team, and the systemic impact of staffing crises on all levels of nursing. It shows how a manager’s burnout can further exacerbate team burnout.
Each distinct case study on nurse burnout offers a unique window into the lived reality of this complex issue, providing rich, contextualized data.
Interventions Informed by a Nurse Burnout Case Study
The ultimate goal of conducting a case study on nurse burnout is not just academic understanding, but to inform tangible actions and interventions that can alleviate and prevent burnout.
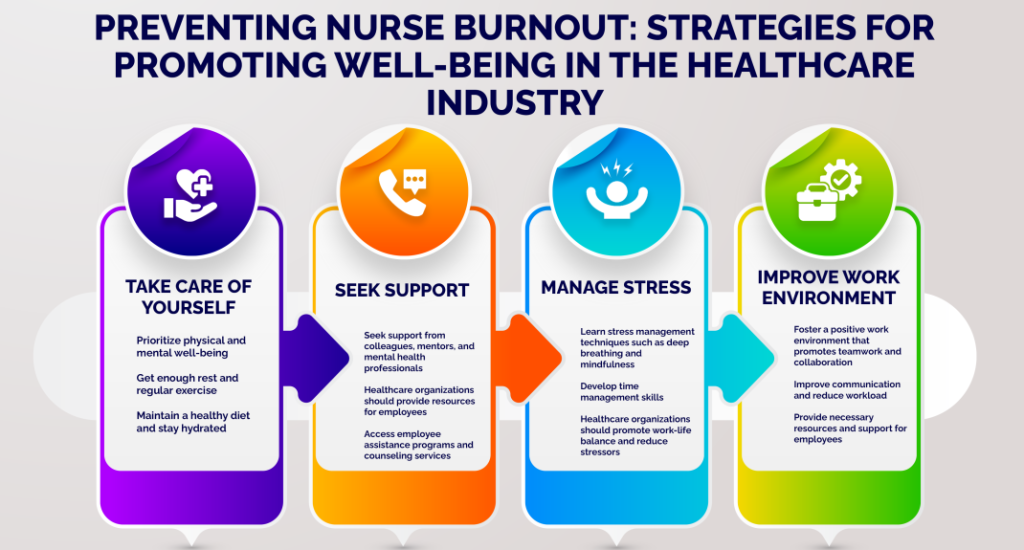
Check out the following example of an intervention to decrease nurse burnout
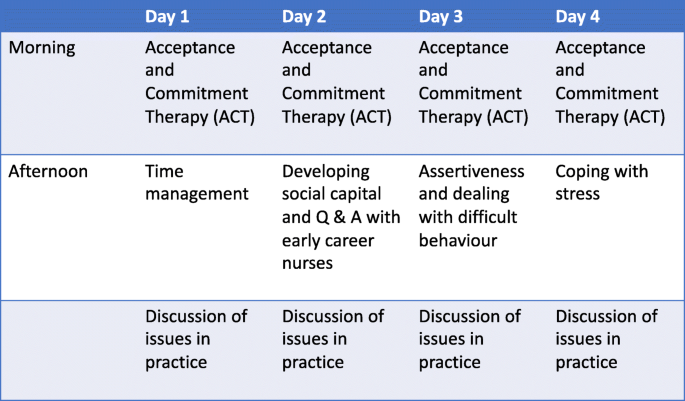
- Individual-Level Interventions:
- While not a solution to systemic problems, individual strategies can help nurses cope:
- Mindfulness practices and stress-reduction techniques.
- Resilience-building workshops.
- Encouraging peer support groups and mentorship.
- Training in boundary setting and self-advocacy.
- Promoting self-care (exercise, nutrition, sleep).
- While not a solution to systemic problems, individual strategies can help nurses cope:
- Organizational-Level Interventions:
- Findings from a detailed case study on nurse burnout can provide compelling evidence for organizational changes:
- Adequate Staffing and Workload Management: Implementing safe nurse-to-patient ratios, ensuring adequate break times, and managing overtime.
- Fostering a Supportive Work Environment: Promoting a culture of respect, appreciation, and psychological safety. Encouraging open communication and teamwork.
- Providing Access to Mental Health Resources: Easily accessible and confidential counseling services, employee assistance programs (EAPs), and debriefing sessions after critical incidents.
- Empowering Nurses and Increasing Autonomy: Involving nurses in decision-making processes related to their practice and work environment.
- Leadership Training for Managers: Equipping nurse managers with skills to support their teams, recognize signs of burnout, and advocate for their staff.
- Recognition Programs: Meaningful acknowledgment of nurses’ contributions.
- Findings from a detailed case study on nurse burnout can provide compelling evidence for organizational changes:
- Systemic Changes:
- Aggregated findings from multiple case study on nurse burnout reports can highlight the need for broader systemic changes:
- Policy Advocacy: Advocating for legislation related to safe staffing, mental health support for healthcare workers, and addressing workplace violence.
- Educational Reform: Better preparing nursing students for the realities of practice and equipping them with coping strategies.
- Addressing Systemic Inequities: Recognizing how factors like underfunding in certain healthcare sectors can exacerbate burnout.
- Aggregated findings from multiple case study on nurse burnout reports can highlight the need for broader systemic changes:
A proactive approach, deeply informed by the nuanced understanding gained from each case study on nurse burnout, is essential for creating sustainable improvements in nurse well-being.
Crafting Your Own Narrative
For students, researchers, or even reflective practitioners, documenting a case study on nurse burnout can be a powerful exercise. Effective nursing case study writing requires a blend of storytelling and academic rigor.
- Structure of a Case Study Report:
- Introduction: Clearly state the problem (nurse burnout), its significance, the purpose of the case study on nurse burnout, and the specific research questions.
- Literature Review: Provide a background on nurse burnout, existing theories, and relevant research, demonstrating how your case study fits into the broader body of knowledge.
- Methodology: Detail how the case study on nurse burnout was conducted – the design (single/multiple), participant selection, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. Ethical considerations should also be outlined.
- Findings/Results: Present the data objectively. This often involves weaving narrative excerpts (direct quotes) with thematic descriptions. Maintain anonymity.
- Discussion: Interpret the findings. How do they answer the research questions? How do they relate to the literature? What are the implications of this particular case study on nurse burnout? Discuss limitations.
- Conclusion and Recommendations: Summarize the key insights and suggest potential actions, interventions, or areas for further research based on the findings of your case study on nurse burnout.
- Tips for Effective Nursing Case Study Writing:
- Tell a Compelling Story: While maintaining academic integrity, allow the participant’s voice and experience to come through.
- Protect Anonymity Rigorously: Use pseudonyms and alter any identifying details.
- Use Direct Quotes Effectively: Illustrate themes and provide rich evidence with carefully selected quotes.
- Maintain Objectivity and Reflexivity: Acknowledge potential biases and strive for a balanced presentation.

If you ever need help with a case study on nurse burnout, Nursing Papers offers professional support. We deliver comprehensive help that covers nursing case study writing, proofreading, editing, formatting and plagiarism removal. Our services also extend to assignments, term papers, proctored exams, TEAS tests, essays, research papers and dissertations.
The Evolving Landscape: Future Directions for Nurse Burnout Research
While much is known about nurse burnout, the evolving nature of healthcare means that research must continue. A case study on nurse burnout remains a vital tool for exploring new and emerging facets of this issue.
- Gaps in Current Research:
- A case study on nurse burnout could explore burnout in underrepresented nursing populations (e.g., male nurses, nurses from minority ethnic groups, nurses in rural or remote settings).
- Investigating burnout in specific, less-studied specialties (e.g., school nursing, forensic nursing, public health nursing).
- Longitudinal case studies are needed to track the trajectory of burnout over time within individuals, and to assess the long-term effectiveness of interventions.
- The impact of new technologies, such as AI in healthcare and increased telehealth, on nurse workload and well-being is a ripe area for a new case study on nurse burnout.
- Comparative case studies looking at burnout experiences and organizational responses across different countries and healthcare systems could yield valuable insights.
- Exploring the “post-pandemic” burnout landscape through a focused case study on nurse burnout is crucial.
Conclusion: Championing Nurse Well-being Through Understanding
Nurse burnout is not an individual failing but a systemic issue with profound consequences. It demands our urgent attention, empathy, and action. Throughout this guide, we have emphasized the invaluable role that a case study on nurse burnout plays in this endeavor. By providing deep, contextual, and human-centered understanding, the case study on nurse burnout methodology allows us to move beyond surface-level statistics and truly grasp the lived realities of nurses facing this challenge.